 B
B C
C D
D E
E F
F G
G H
H I
I J
J K
K L
L M
M N
N O
O P
P Q
Q R
R S
S T
T U
U V
V W
W X
X Y
Y Z
A ↑
Z
A ↑
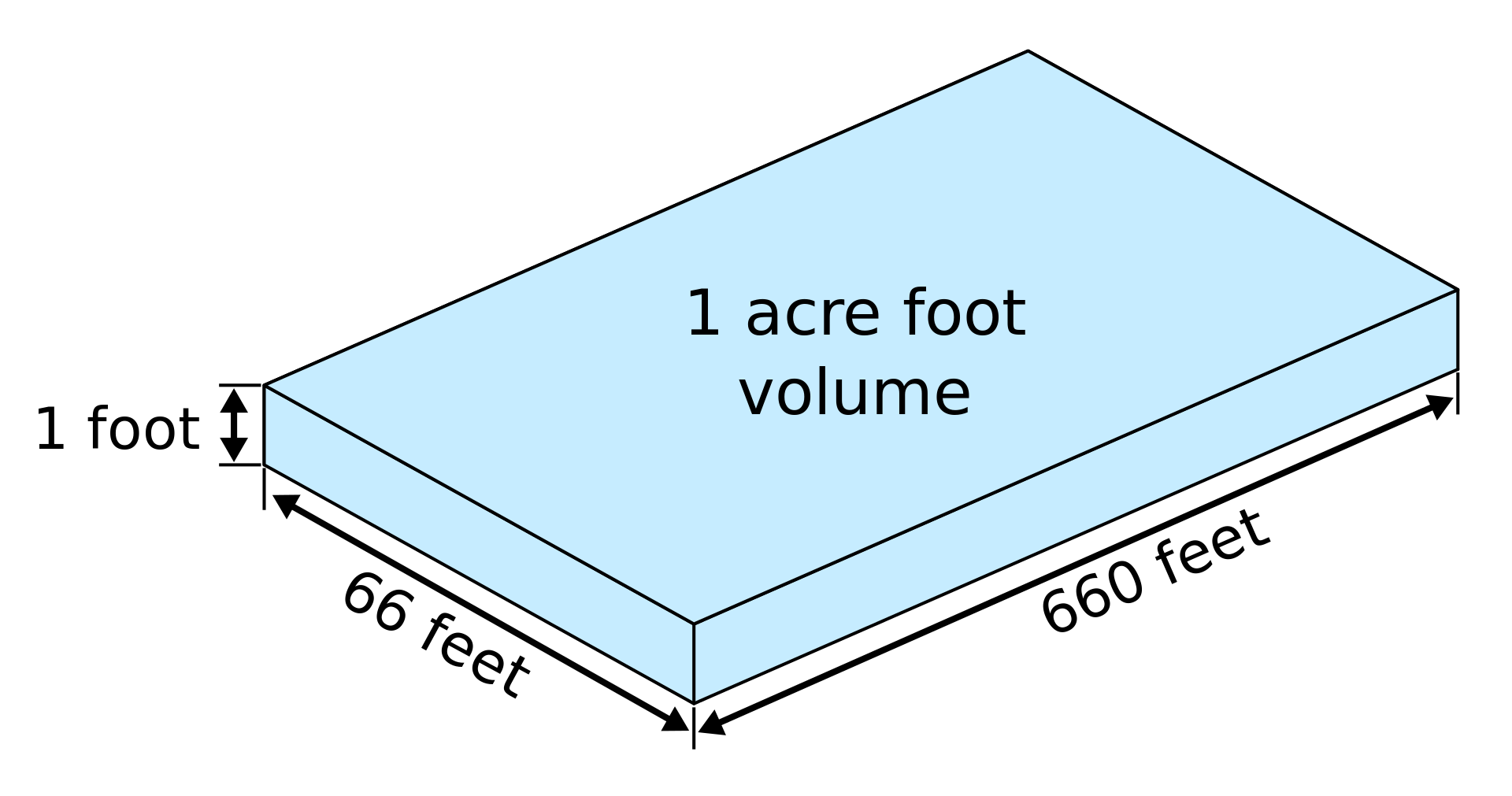
 AFY
acre-feet per year
AFY
acre-feet per yearAMA active management areaareas with heavy reliance on mined groundwater identified and designated by the 1980 Arizona Groundwater Management Act, as the Prescott, Phoenix, Pinal, Tucson, and Santa Cruz management areas, where groundwater is subject to state regulation AMOC Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation AMSL above mean sea level AMWUA Arizona Municipal Water Users Association ANSAC Arizona Navigable Streams Adjudication Commission APEC Advisory Panel on Emerging Contaminants APP aquifer protection permit ARC Arizona Reconsultation Committee ASLD Arizona State Land Department ASR aquifer storage and recovery ASTM American Society for Testing and Materials What are the 3 rock classifications? ATW advanced treated water AVRP Avra Valley Recharge Project AVWU Arizona Virtual Water University AWBA Arizona Water Banking Authority What branch of science studies the relations between heat and other forms of energy? AWIA America's Water Infrastructure Act AWPF Arizona Water Protection Fund AWQS aquifer water quality standards AWRA American Water Resources Association What are Earth`s 5 main soil layers? AWRC Arizona Water Resources Committee AWS Assured Water Supply AWSA Arizona Water Settlements Act What are the 8 Linnaean classification levels? AWT advanced wastewater treatmentany process that can reduce impurities in wastewater below what is attainable through conventional secondary or biological treatment AWTF advanced water treatment facility AWWA American Water Works Association AWWT advanced wastewater treatment What is the difference between climate and weather? AZPDES Arizona Pollutant Discharge Elimination System AZMET Arizona Meteorological Network AZWIFA Water Infrastructure Finance Authority of Arizona B ↑

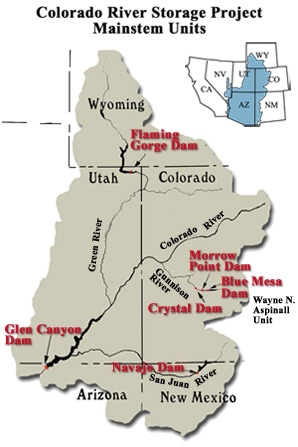
 CRSP
Colorado River Storage Project
CRSS
Colorado River Simulation System
CRWUA
Colorado River Water Users Association
CSIF
CAP/SRP Interconnection Facility
CTPP
Central Tucson PFAS Project
CVWD
Coachella Valley Water District
CWA
Clean Water Act
CWCCG
California Wastewater Climate Change Group
CWISA
Clean Water Indian Set Aside
CWS
community water systema public water system that supplies water to the same population for the entire year
D ↑
DALY
disability adjusted life yearsage-standardized disability-adjusted life-years lost per 100,000 persons due to exposure to unsafe drinking water
DAWS
designation of assured water supplyissued to water providers to demonstrate that water of sufficient quantity and quality is legally available to serve the proposed development for 100 years
DBP
disinfection byproductsalso called trihalomethanes, formed when chlorine and bromine interact with natural organic materials in water
DBPR
Disinfection Byproduct Rules
DCDC
Decision Center for a Desert City
What South Pacific surface temperature anomalies influence weather on a large scale?
DCE
dichloroethanea clear, colorless liquid used to make vinyl chloride and other chemicals and as a solvent, degreaser and wetting agent
DCP
Drought Contingency Plan
DLCC
Desert Landscape Conservation Cooperative
DMR
Discharge Monitoring Report
CRSP
Colorado River Storage Project
CRSS
Colorado River Simulation System
CRWUA
Colorado River Water Users Association
CSIF
CAP/SRP Interconnection Facility
CTPP
Central Tucson PFAS Project
CVWD
Coachella Valley Water District
CWA
Clean Water Act
CWCCG
California Wastewater Climate Change Group
CWISA
Clean Water Indian Set Aside
CWS
community water systema public water system that supplies water to the same population for the entire year
D ↑
DALY
disability adjusted life yearsage-standardized disability-adjusted life-years lost per 100,000 persons due to exposure to unsafe drinking water
DAWS
designation of assured water supplyissued to water providers to demonstrate that water of sufficient quantity and quality is legally available to serve the proposed development for 100 years
DBP
disinfection byproductsalso called trihalomethanes, formed when chlorine and bromine interact with natural organic materials in water
DBPR
Disinfection Byproduct Rules
DCDC
Decision Center for a Desert City
What South Pacific surface temperature anomalies influence weather on a large scale?
DCE
dichloroethanea clear, colorless liquid used to make vinyl chloride and other chemicals and as a solvent, degreaser and wetting agent
DCP
Drought Contingency Plan
DLCC
Desert Landscape Conservation Cooperative
DMR
Discharge Monitoring Report






 B
B C
C D
D E
E F
F G
G H
H I
I J
J K
K L
L M
M N
N O
O P
P Q
Q R
R S
S T
T U
U V
V W
W X
X Y
Y Z
A ↑
Approximately 21% of Earth`s atmosphere is what gas?
absolute humidity
measure of the actual amount of water vapor in the air, regardless of air temperature
abyssal hill
a hill that rises from the sea floor
abyssal plain
an underwater plain on the deep ocean floor
abyssopelagic zone
from the bottom of the bathypelagic to the seafloor, characterized by a relative lack of life
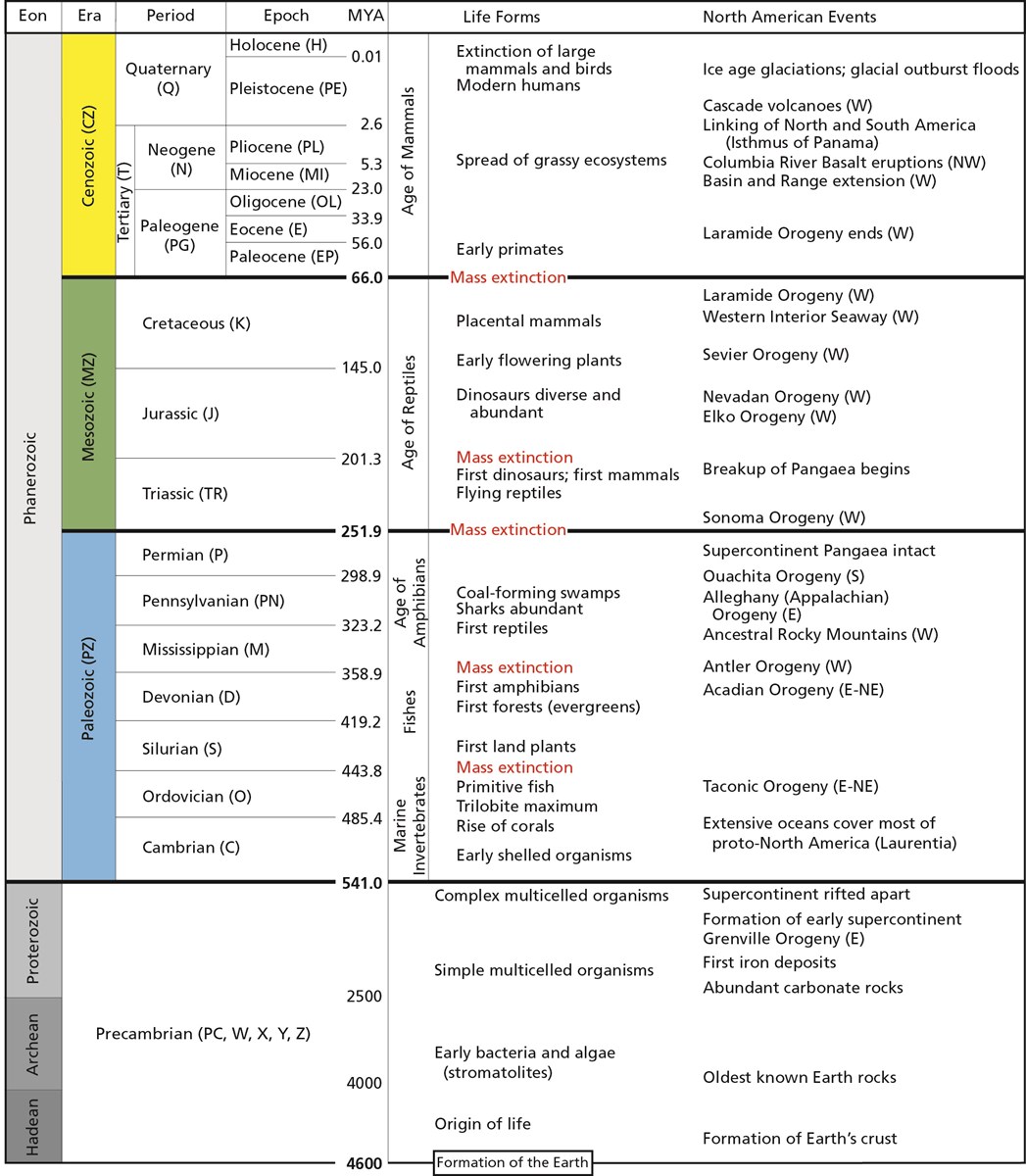
What are the 2 periods of the Cenozoic era?
acequia
gravity-driven waterway similar to a flume
acid
refers to a substance with a pH less than 7
acid rain
rain with low pH
Z
A ↑
Approximately 21% of Earth`s atmosphere is what gas?
absolute humidity
measure of the actual amount of water vapor in the air, regardless of air temperature
abyssal hill
a hill that rises from the sea floor
abyssal plain
an underwater plain on the deep ocean floor
abyssopelagic zone
from the bottom of the bathypelagic to the seafloor, characterized by a relative lack of life
What are the 2 periods of the Cenozoic era?
acequia
gravity-driven waterway similar to a flume
acid
refers to a substance with a pH less than 7
acid rain
rain with low pH

 advanced drinking water treatment (ADWT)
additional engineered treatment after secondary or tertiary treatment of wastewater to remove contaminants of concern to make it acceptable for drinking water purposes
advanced oxidation
use of ozone, ultraviolet light and hydrogen peroxide to for pathogen disinfection and organic contaminant removal
advanced wastewater treatment (AWT)
any process that can reduce impurities in wastewater below what is attainable through conventional secondary or biological treatment
advection
movement of water through the atmosphere
adenine
one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acids of DNA
aeolian
related to or produced by wind
aerosol
a substance enclosed under pressure and able to be released as a fine spray, typically by using a propellant gas
age
smallest geochronologic unit
agriculture
the science or practice of farming
agrivoltaics
the simultaneous use of land areas for solar panels and agriculture
advanced drinking water treatment (ADWT)
additional engineered treatment after secondary or tertiary treatment of wastewater to remove contaminants of concern to make it acceptable for drinking water purposes
advanced oxidation
use of ozone, ultraviolet light and hydrogen peroxide to for pathogen disinfection and organic contaminant removal
advanced wastewater treatment (AWT)
any process that can reduce impurities in wastewater below what is attainable through conventional secondary or biological treatment
advection
movement of water through the atmosphere
adenine
one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acids of DNA
aeolian
related to or produced by wind
aerosol
a substance enclosed under pressure and able to be released as a fine spray, typically by using a propellant gas
age
smallest geochronologic unit
agriculture
the science or practice of farming
agrivoltaics
the simultaneous use of land areas for solar panels and agriculture






 basement
crystalline rocks lying above the mantle and beneath all other rocks and sediments
basic sector
the primary markets for locally produced goods and services lay outside of that county
basin
a land area that drains into a common outlet
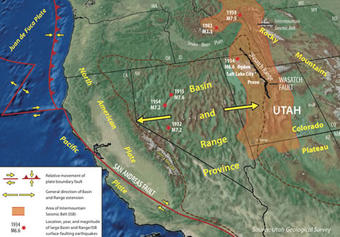
Basin and Range Province
a large region covering part of the inland Western U.S. and northwestern Mexico that is characterized by abrupt changes in elevation, alternating between narrow faulted mountain chains and flat arid valleys or basins
basin sweep
systematic collection of well water, groundwater and water quality data by ADWR
batholith
a large mass of intrusive igneous rock larger than 100 square kilometers that forms from cooled magma deep in Earth's crust
bathypelagic zone
lower open ocean, starts at the bottom of the mesopelagic and stretches down to 4000 m (13,000 feet)
bay
a water body partially surrounded by land and by another water body
bayou
a marsh-like outlet of a lake or river
basement
crystalline rocks lying above the mantle and beneath all other rocks and sediments
basic sector
the primary markets for locally produced goods and services lay outside of that county
basin
a land area that drains into a common outlet
Basin and Range Province
a large region covering part of the inland Western U.S. and northwestern Mexico that is characterized by abrupt changes in elevation, alternating between narrow faulted mountain chains and flat arid valleys or basins
basin sweep
systematic collection of well water, groundwater and water quality data by ADWR
batholith
a large mass of intrusive igneous rock larger than 100 square kilometers that forms from cooled magma deep in Earth's crust
bathypelagic zone
lower open ocean, starts at the bottom of the mesopelagic and stretches down to 4000 m (13,000 feet)
bay
a water body partially surrounded by land and by another water body
bayou
a marsh-like outlet of a lake or river


 bioluminescence
biochemical emission of light by living organisms such as fireflies and deep-sea fish
biomagnification
build up of toxins in a food chain
biomass
total quantity or weight of organisms in a given area or volume
biomatter
mass of living matter within a given area
biome
a large naturally occurring community of flora and fauna occupying a major habitat
biosolids
organic matter recycled from sewage
biosorption
a natural chemical process that allows the binding and concentration of contaminants
biosphere
the regions of the surface, atmosphere, and hydrosphere occupied by living organisms
bioluminescence
biochemical emission of light by living organisms such as fireflies and deep-sea fish
biomagnification
build up of toxins in a food chain
biomass
total quantity or weight of organisms in a given area or volume
biomatter
mass of living matter within a given area
biome
a large naturally occurring community of flora and fauna occupying a major habitat
biosolids
organic matter recycled from sewage
biosorption
a natural chemical process that allows the binding and concentration of contaminants
biosphere
the regions of the surface, atmosphere, and hydrosphere occupied by living organisms






 climate change
a change in global or regional climate patterns, in particular a change apparent from the mid to late 20th century onwards and attributed largely to the increased levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide produced by the use of fossil fuels
climate change mitigation
action to limit climate change by reducing emissions of greenhouse gases or removing those gases from the atmosphere
climatology
the scientific study of climate
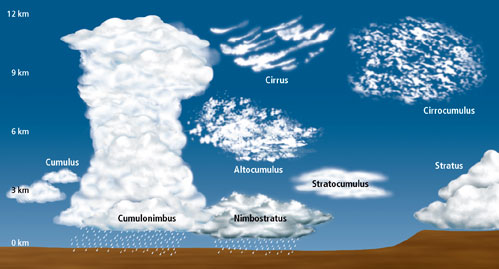
cloud classification
system that classifies cloud types by altitude
coastal flood
result of coastal storms, including hurricanes or nor'easters that create destructive storm surges, walls of water moving from ocean onto land
cobaltocene
an organocobalt compound with the formula Co(C5H5)2
cognition
the mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses
climate change
a change in global or regional climate patterns, in particular a change apparent from the mid to late 20th century onwards and attributed largely to the increased levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide produced by the use of fossil fuels
climate change mitigation
action to limit climate change by reducing emissions of greenhouse gases or removing those gases from the atmosphere
climatology
the scientific study of climate
cloud classification
system that classifies cloud types by altitude
coastal flood
result of coastal storms, including hurricanes or nor'easters that create destructive storm surges, walls of water moving from ocean onto land
cobaltocene
an organocobalt compound with the formula Co(C5H5)2
cognition
the mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses
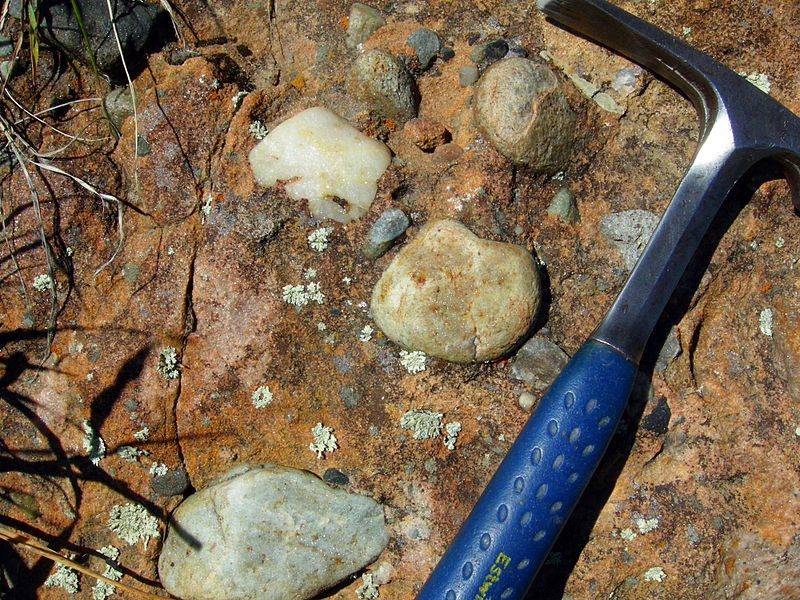


 conglomerate
a coarse-grained clastic sedimentary rock that is composed of a substantial fraction of rounded to subangular gravel-size clasts larger than 2 millimeters in diameter
conjugate acid
has the hydronium ion, H3O+, as its base
conodont
a fossil marine animal of the Cambrian to Triassic periods, having a long wormlike body, numerous small teeth and a pair of eyes, may be the earliest vertebrate
conservation effluent pool (CEP)
effluent set aside each year pursuant to an intergovernmental agreement between the City of Tucson and Pima County for use in riparian restoration projects
conservation efforts report (CER)
filed by large municipal water providers
constructed recharge
replenishing the aquifer using a facility that is designed and constructed, in-channel, or off-channel, to store water underground pursuant to permits issued by ADWR
consumptive use
water that is evaporated, used by plants and crops and consumed by animals and humans
contaminant candidate list (CCL)
a list of contaminants in public water systems currently not subject to proposed national primary drinking water regulations, that may concern the public
conglomerate
a coarse-grained clastic sedimentary rock that is composed of a substantial fraction of rounded to subangular gravel-size clasts larger than 2 millimeters in diameter
conjugate acid
has the hydronium ion, H3O+, as its base
conodont
a fossil marine animal of the Cambrian to Triassic periods, having a long wormlike body, numerous small teeth and a pair of eyes, may be the earliest vertebrate
conservation effluent pool (CEP)
effluent set aside each year pursuant to an intergovernmental agreement between the City of Tucson and Pima County for use in riparian restoration projects
conservation efforts report (CER)
filed by large municipal water providers
constructed recharge
replenishing the aquifer using a facility that is designed and constructed, in-channel, or off-channel, to store water underground pursuant to permits issued by ADWR
consumptive use
water that is evaporated, used by plants and crops and consumed by animals and humans
contaminant candidate list (CCL)
a list of contaminants in public water systems currently not subject to proposed national primary drinking water regulations, that may concern the public


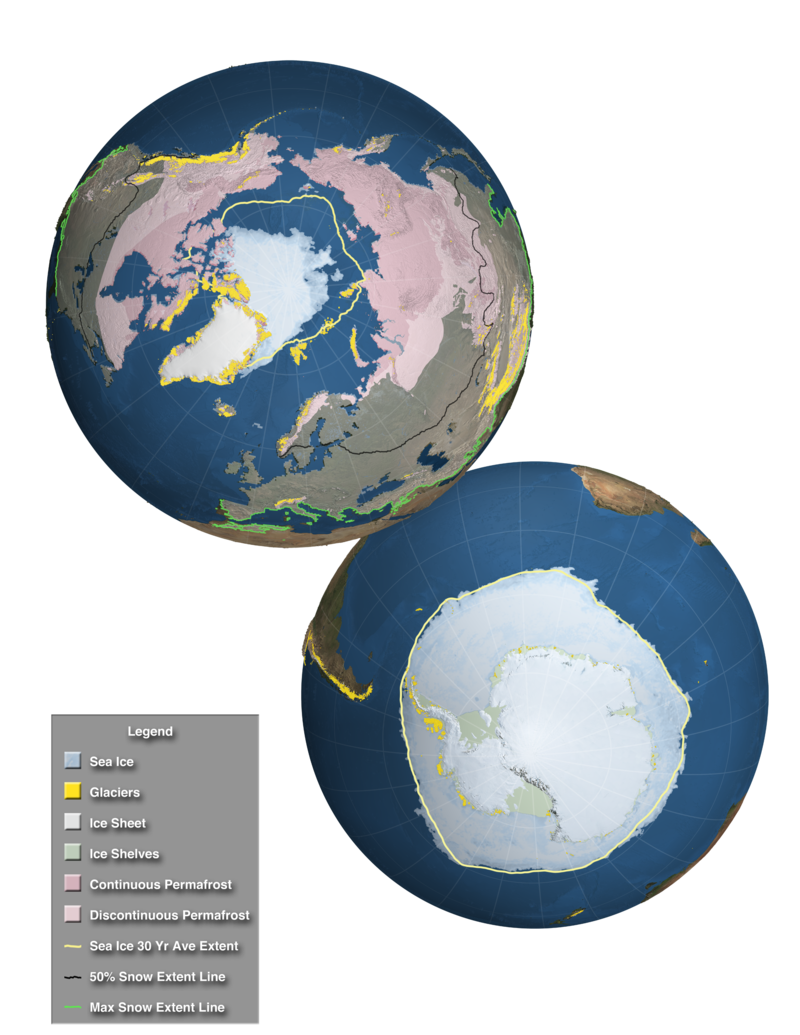
 cryosphere
portions of a planet's surface where water is solid, including sea ice, lake ice, river ice, snow cover, glaciers, ice caps, ice sheets, and frozen ground
cryptosporidium
a parasitic alveolate that can cause respiratory and gastrointestinal illness
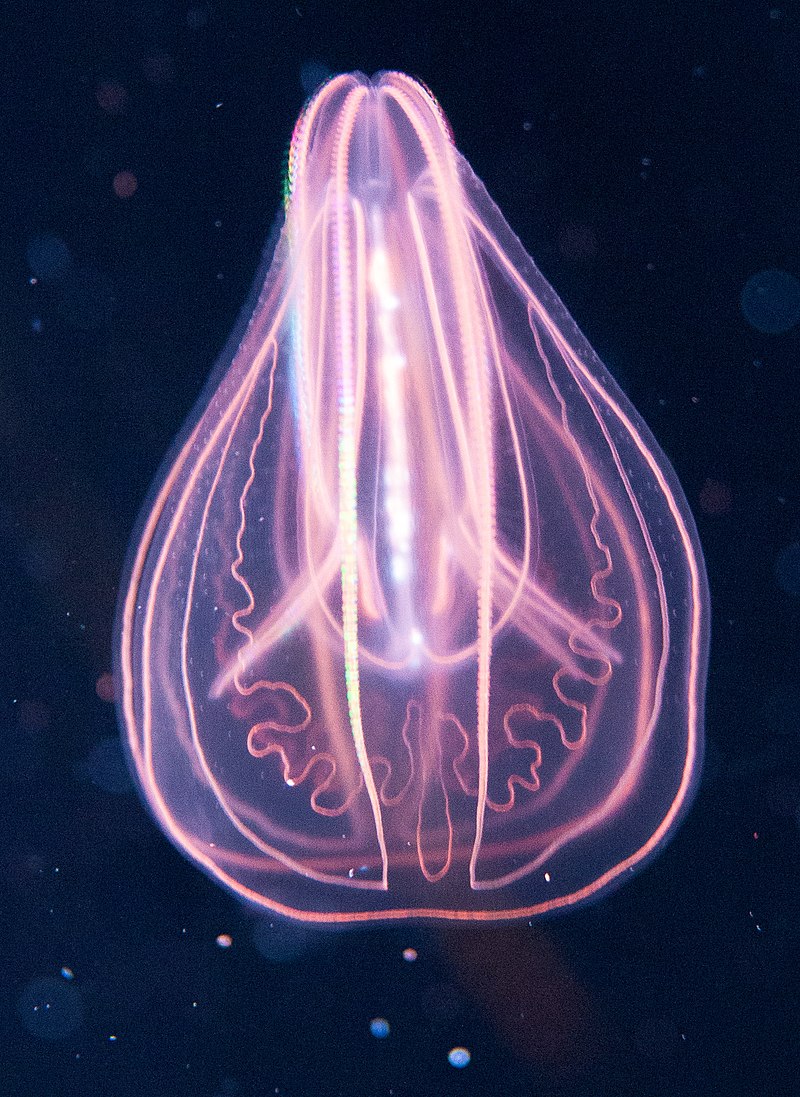
Ctenophore
also known as a comb jelly, may be Earth's most ancient creature
cultivation
preparing soil for crop planting
cultural water demand
includes water diverted, pumped from wells, or received to meet municipal, industrial and agricultural demands
culvert
structure that allows water to flow under a road, railroad, trail or other obstruction
cumulonimbus
cloud forming a towering mass with a flat base at fairly low altitude and often a flat top, as in thunderstorms
cumulus
cloud forming rounded masses heaped on each other above a flat base at fairly low altitude
curb cut
allows stormwater from the street to flow into water-harvesting basins to irrigate vegetation
cyanide
a large group of poisonous chemical compounds used to make plastics and to extract and treat metals
cyclogenesis
refers to the formation process of a low-pressure area
cyclone
a tropical storm in the region of the Indian Ocean and South Pacific
cryosphere
portions of a planet's surface where water is solid, including sea ice, lake ice, river ice, snow cover, glaciers, ice caps, ice sheets, and frozen ground
cryptosporidium
a parasitic alveolate that can cause respiratory and gastrointestinal illness
Ctenophore
also known as a comb jelly, may be Earth's most ancient creature
cultivation
preparing soil for crop planting
cultural water demand
includes water diverted, pumped from wells, or received to meet municipal, industrial and agricultural demands
culvert
structure that allows water to flow under a road, railroad, trail or other obstruction
cumulonimbus
cloud forming a towering mass with a flat base at fairly low altitude and often a flat top, as in thunderstorms
cumulus
cloud forming rounded masses heaped on each other above a flat base at fairly low altitude
curb cut
allows stormwater from the street to flow into water-harvesting basins to irrigate vegetation
cyanide
a large group of poisonous chemical compounds used to make plastics and to extract and treat metals
cyclogenesis
refers to the formation process of a low-pressure area
cyclone
a tropical storm in the region of the Indian Ocean and South Pacific

 deposition (chemistry)
transition of a substance directly from the gas to the solid phase, without passing through the intermediate liquid phase
deposition (geology)
process in which sediments, soil and rocks are added to existing layers of sediments, soil or rock
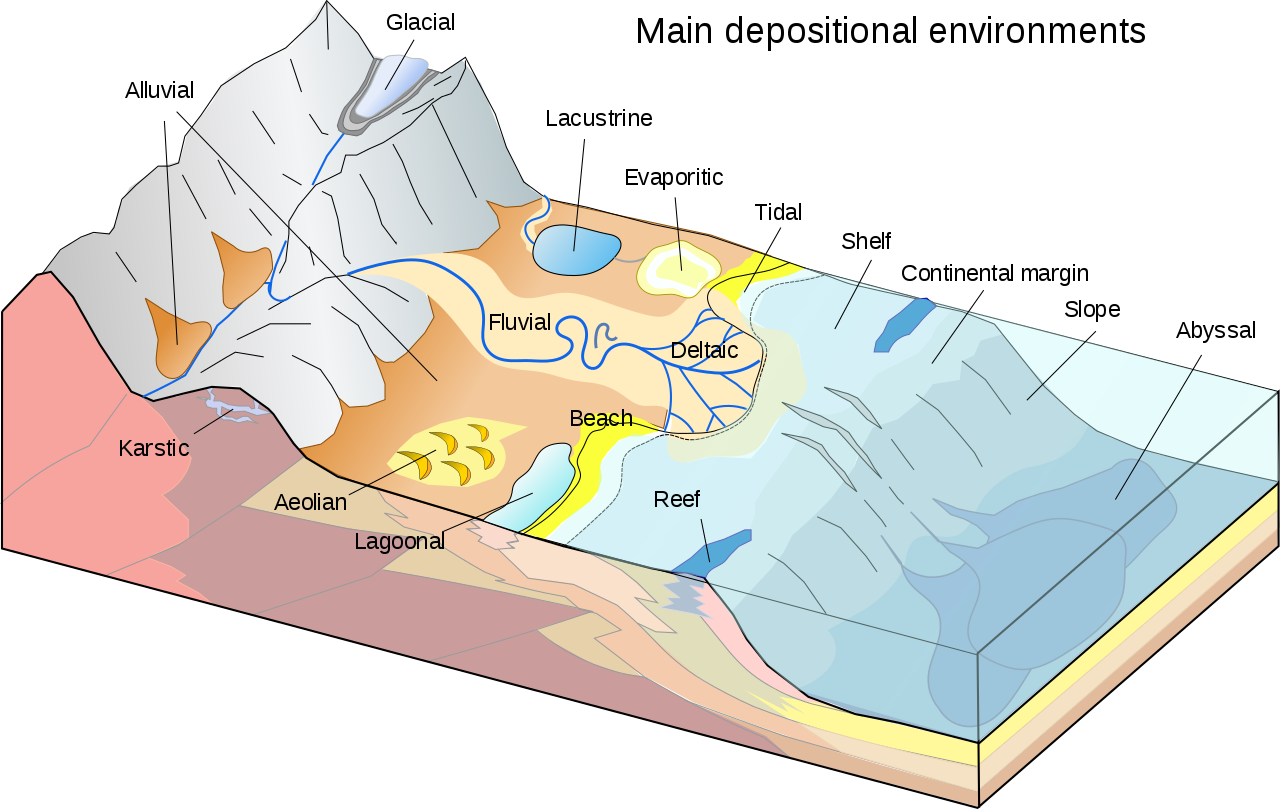
depositional environment
a setting in which a sedimentary rock forms
desalination
process of removing salt from seawater
desert
a dry region receiving less than 12 inches of annual precipitation and formed when regional climate changes result in long-lasting drought conditions
desertification
process by which fertile land becomes desert, usually drought, deforestation or poor agricultural practices
desert pavement
a surface layer of closely packed or cemented pebbles and rock fragments from which fine material has been removed by the wind in arid regions
desert varnish
a dark hard film of rusty-looking rock formed on exposed rock surfaces in arid regions
designation of assured water supply (DAWS)
issued to water suppliers to demonstrate that water of sufficient quantity and quality is legally available to serve the proposed development for 100 years
detritus
gravel, sand, silt, or other material produced by erosion or organic matter produced by the decomposition of organisms
deuterium
isotope of hydrogen with a nucleus consisting of one proton and one neutron
deposition (chemistry)
transition of a substance directly from the gas to the solid phase, without passing through the intermediate liquid phase
deposition (geology)
process in which sediments, soil and rocks are added to existing layers of sediments, soil or rock
depositional environment
a setting in which a sedimentary rock forms
desalination
process of removing salt from seawater
desert
a dry region receiving less than 12 inches of annual precipitation and formed when regional climate changes result in long-lasting drought conditions
desertification
process by which fertile land becomes desert, usually drought, deforestation or poor agricultural practices
desert pavement
a surface layer of closely packed or cemented pebbles and rock fragments from which fine material has been removed by the wind in arid regions
desert varnish
a dark hard film of rusty-looking rock formed on exposed rock surfaces in arid regions
designation of assured water supply (DAWS)
issued to water suppliers to demonstrate that water of sufficient quantity and quality is legally available to serve the proposed development for 100 years
detritus
gravel, sand, silt, or other material produced by erosion or organic matter produced by the decomposition of organisms
deuterium
isotope of hydrogen with a nucleus consisting of one proton and one neutron
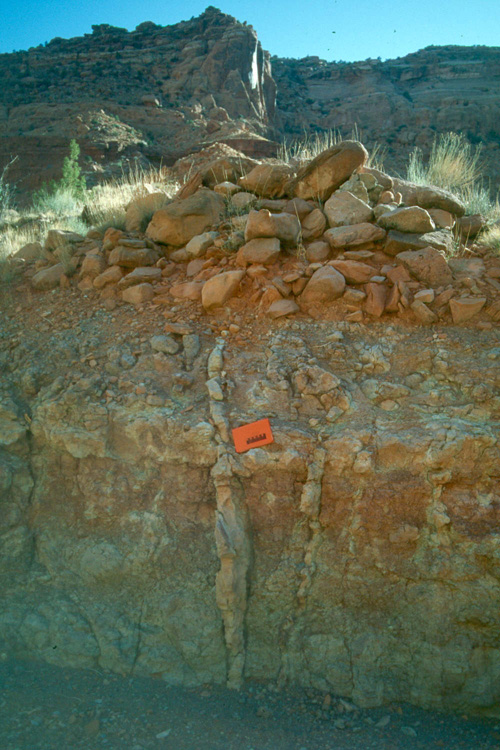


 discharge
volume of water that passes a give location in a given time period
disconformity
an unconformity between parallel layers of sedimentary rocks which represents a period of erosion or non-deposition
disinfection
treatment of water to inactivate, destroy, and/or remove disease-producing bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms
disinfection by-product (DBP)
result from chemical reactions between organic and inorganic matter in water with chemical treatment agents during the water disinfection process
dissolution
the action or process of dissolving or being dissolved
dissolved oxygen
amount of oxygen present in water
distillation
the process of separating parts of a liquid substance through boiling and condensation
distilled water
water from which impurities, such as dissolved salts and colloidal particles, have been removed
distributary
a branch of a river that does not return to the main stream after leaving it
divergent boundary
a linear feature between tectonic plates moving away from each other
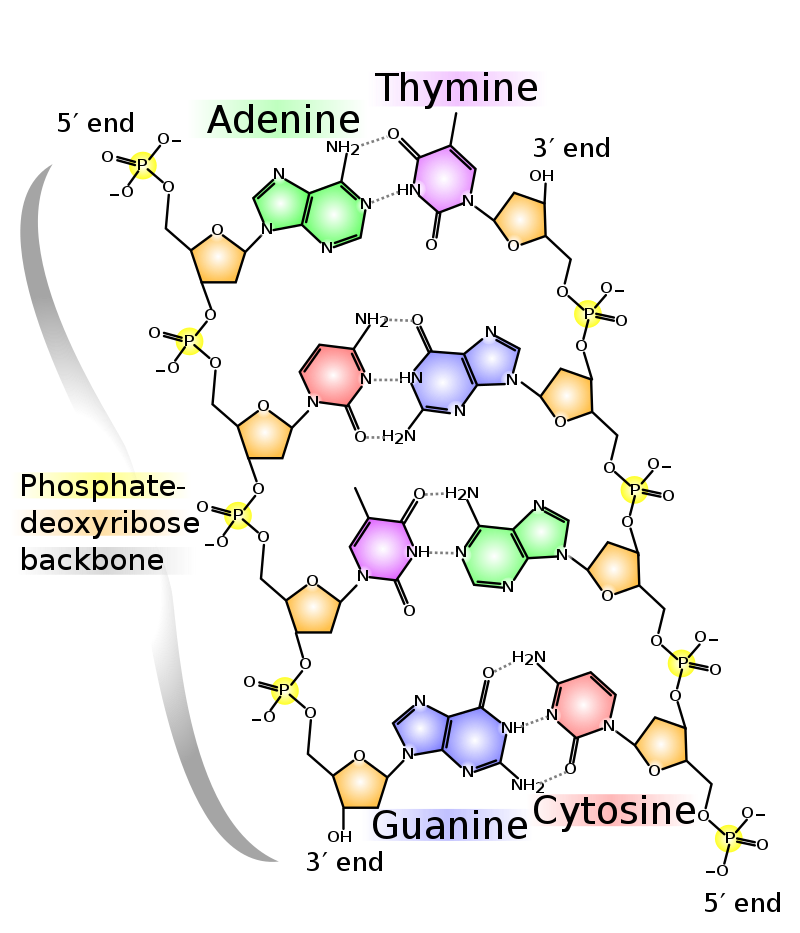
DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid, a self-replicating material present in nearly all living organisms as the main constituent of chromosomes, carrier of genetic information.
doctrine of prior appropriation
the person who first puts the water to a beneficial use acquires a right that is better than later appropriators of the water
doldrums
an equatorial region of the Atlantic Ocean with calms, sudden storms and light unpredictable winds
dolerite
a fine- to medium-grained, dark gray to black intrusive igneous rock
domestic use
uses related to supply, service, and activities of households and private residences, including water for less than two acres of land
to produce plants for human or animal consumption
discharge
volume of water that passes a give location in a given time period
disconformity
an unconformity between parallel layers of sedimentary rocks which represents a period of erosion or non-deposition
disinfection
treatment of water to inactivate, destroy, and/or remove disease-producing bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms
disinfection by-product (DBP)
result from chemical reactions between organic and inorganic matter in water with chemical treatment agents during the water disinfection process
dissolution
the action or process of dissolving or being dissolved
dissolved oxygen
amount of oxygen present in water
distillation
the process of separating parts of a liquid substance through boiling and condensation
distilled water
water from which impurities, such as dissolved salts and colloidal particles, have been removed
distributary
a branch of a river that does not return to the main stream after leaving it
divergent boundary
a linear feature between tectonic plates moving away from each other
DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid, a self-replicating material present in nearly all living organisms as the main constituent of chromosomes, carrier of genetic information.
doctrine of prior appropriation
the person who first puts the water to a beneficial use acquires a right that is better than later appropriators of the water
doldrums
an equatorial region of the Atlantic Ocean with calms, sudden storms and light unpredictable winds
dolerite
a fine- to medium-grained, dark gray to black intrusive igneous rock
domestic use
uses related to supply, service, and activities of households and private residences, including water for less than two acres of land
to produce plants for human or animal consumption

 domestic water improvement district (DWID)
formed to construct or improve a domestic water delivery system or to purchase an existing domestic water delivery system
domestic well
a small capacity well used for domestic water use
Dominy formation
a layer of Colorado River sediment in Lake Powell, estimated to be at least 100 feet thick
down-cutting
water flow that deepens a channel of a stream or valley by removing material from the stream's bed or the valley's floor
drag fold
a minor geological fold produced in soft roc beds between harder rocks
drainage basin
an area of land where precipitation collects and drains into a common outlet, such as a river, bay or other body of water
drawdown
lowering of groundwater due to water pumping
domestic water improvement district (DWID)
formed to construct or improve a domestic water delivery system or to purchase an existing domestic water delivery system
domestic well
a small capacity well used for domestic water use
Dominy formation
a layer of Colorado River sediment in Lake Powell, estimated to be at least 100 feet thick
down-cutting
water flow that deepens a channel of a stream or valley by removing material from the stream's bed or the valley's floor
drag fold
a minor geological fold produced in soft roc beds between harder rocks
drainage basin
an area of land where precipitation collects and drains into a common outlet, such as a river, bay or other body of water
drawdown
lowering of groundwater due to water pumping

 drip irrigation
an irrigation method that uses pipes that allow water to drip slowly onto plants
drop
a small column of liquid, bounded completely or almost completely by free surfaces
drought
a sustained natural reduction in precipitation that results in negative environmental and human impacts
dry lake
a basin that used to contain a lake, but is now dry
dry system
refers to thepipework allowing rainwater to flow from a roof into a rainwater tank, after a downpour no water is retained in the pipes
drying reef
a part of a reef which is above water at low tide but submerged at high tide
dwarf planet
a small planetary object that orbits the Sun but is too small to be classified as a planet
dynamically stable beach
formed using breakwaters, jetties, impermeable groynes or seawalls
E ↑
Eastern Hemisphere
the half of Earth east of the prime meridian at Greenwich, London, United Kingdom and west of the antimeridian which crosses the Pacific Ocean and relatively little land from pole to pole
echinoderm
any of a variety of invertebrate marine animals belonging to the phylum Echinodermata, characterized by a hard, spiny covering or skin
eclogite
a metamorphic rock consisting of pyroxene omphacite and pyrope-rich garnet
ecohydrology
the study of the interactions between water and ecological systems
drip irrigation
an irrigation method that uses pipes that allow water to drip slowly onto plants
drop
a small column of liquid, bounded completely or almost completely by free surfaces
drought
a sustained natural reduction in precipitation that results in negative environmental and human impacts
dry lake
a basin that used to contain a lake, but is now dry
dry system
refers to thepipework allowing rainwater to flow from a roof into a rainwater tank, after a downpour no water is retained in the pipes
drying reef
a part of a reef which is above water at low tide but submerged at high tide
dwarf planet
a small planetary object that orbits the Sun but is too small to be classified as a planet
dynamically stable beach
formed using breakwaters, jetties, impermeable groynes or seawalls
E ↑
Eastern Hemisphere
the half of Earth east of the prime meridian at Greenwich, London, United Kingdom and west of the antimeridian which crosses the Pacific Ocean and relatively little land from pole to pole
echinoderm
any of a variety of invertebrate marine animals belonging to the phylum Echinodermata, characterized by a hard, spiny covering or skin
eclogite
a metamorphic rock consisting of pyroxene omphacite and pyrope-rich garnet
ecohydrology
the study of the interactions between water and ecological systems
 electron
a negatively-charged subatomic particle that orbits atomic nuclei
element
each of more than one hundred substances that cannot be chemically converted or broken down into simpler substances and which are primary constituents of matter
elevation
height above a given level, especially sea level
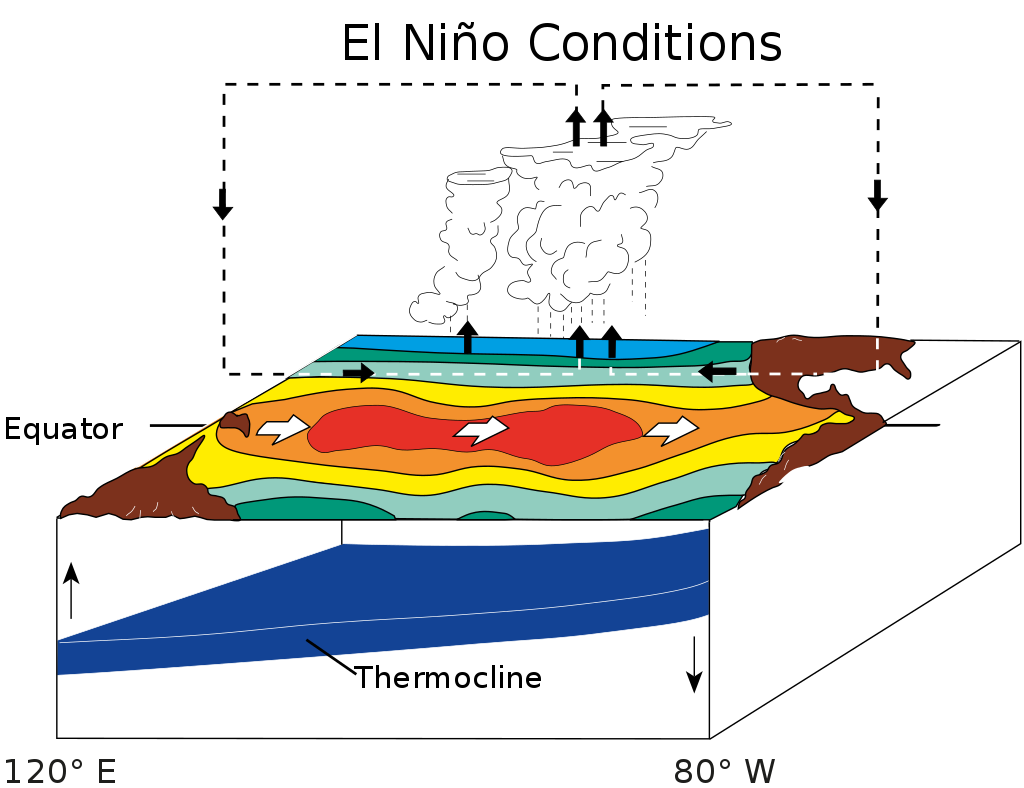
El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO)
the cycle of warm and cold sea surface temperature of the tropical central and eastern Pacific Ocean accompanied by high air pressure in the western Pacific and low air pressure in the eastern Pacific
emulsion
a dispersion of minute droplets of one liquid in another in which it is not soluble
endangered species
a species of animal or plant that is seriously at risk of extinction
endorheic basin
inland basin that does not drain to an ocean
engineered storage buffer
storage facility used to provide retention time before advanced treated water is introduced into the drinking water system
environment
the surroundings or conditions in which a person, animal or plant lives
environmental buffer
a groundwater aquifer, surface water reservoir, lake or river in which advanced treated water is introduced before being used for potable reuse
environmental flows
quality, quantity and flowing water timing needed to sustain estuarine ecosystems
environmental impact statement (EIS)
government document that outlines the impact of a proposed project on its surrounding environment
environmental performance index (EPI)
uses 40 performance indicators in 11 issue categories to rank countries on climate change performance, environmental health and ecosystem vitality
environmental restoration
also referred to as riparian restoration, riparian enhancement or habitat restoration, enhancing existing ecosystems or creating new habitat to
recover ecosystem functional characteristics including plant communities and habitat structure
environmental well
a well used to monitor a contamination site
eon
largest formal geochronologic time unit, equivalent of a chronostratigraphic eonothem
eonothem
totality of rock strata deposited during an eon in the geologic timescale
ephemeral stream
a temporary stream that flows as the result of precipitation
electron
a negatively-charged subatomic particle that orbits atomic nuclei
element
each of more than one hundred substances that cannot be chemically converted or broken down into simpler substances and which are primary constituents of matter
elevation
height above a given level, especially sea level
El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO)
the cycle of warm and cold sea surface temperature of the tropical central and eastern Pacific Ocean accompanied by high air pressure in the western Pacific and low air pressure in the eastern Pacific
emulsion
a dispersion of minute droplets of one liquid in another in which it is not soluble
endangered species
a species of animal or plant that is seriously at risk of extinction
endorheic basin
inland basin that does not drain to an ocean
engineered storage buffer
storage facility used to provide retention time before advanced treated water is introduced into the drinking water system
environment
the surroundings or conditions in which a person, animal or plant lives
environmental buffer
a groundwater aquifer, surface water reservoir, lake or river in which advanced treated water is introduced before being used for potable reuse
environmental flows
quality, quantity and flowing water timing needed to sustain estuarine ecosystems
environmental impact statement (EIS)
government document that outlines the impact of a proposed project on its surrounding environment
environmental performance index (EPI)
uses 40 performance indicators in 11 issue categories to rank countries on climate change performance, environmental health and ecosystem vitality
environmental restoration
also referred to as riparian restoration, riparian enhancement or habitat restoration, enhancing existing ecosystems or creating new habitat to
recover ecosystem functional characteristics including plant communities and habitat structure
environmental well
a well used to monitor a contamination site
eon
largest formal geochronologic time unit, equivalent of a chronostratigraphic eonothem
eonothem
totality of rock strata deposited during an eon in the geologic timescale
ephemeral stream
a temporary stream that flows as the result of precipitation


 extinguishment credits
gained when a grandfathered water right is cancelled and can be committed to a water supply
extratropical cyclone
low-pressure areas which drive the weather over much of the Earth, capable of producing clouds, gales, thunderstorms, blizzards and tornadoes
extravasated
let or force out from the vessel that naturally contains it into the surrounding area
extrusive
refers to igneous volcanic rock in which hot magma from inside the Earth flows out onto the surface as lava or explodes violently into the atmosphere to fall back as
pyroclastics or tuff
F ↑
Fahrenheit
temperature scale on which pure water freezing point was defined as 32oF and water boiling point was defined to be 212oF
fallow
a farming technique in which arable land is left without replanting during a planting season
fault
crack in the Earth's crust often associated with boundaries between Earth's tectonic plates
fauna
the animals of a particular region, habitat, or geological period
extinguishment credits
gained when a grandfathered water right is cancelled and can be committed to a water supply
extratropical cyclone
low-pressure areas which drive the weather over much of the Earth, capable of producing clouds, gales, thunderstorms, blizzards and tornadoes
extravasated
let or force out from the vessel that naturally contains it into the surrounding area
extrusive
refers to igneous volcanic rock in which hot magma from inside the Earth flows out onto the surface as lava or explodes violently into the atmosphere to fall back as
pyroclastics or tuff
F ↑
Fahrenheit
temperature scale on which pure water freezing point was defined as 32oF and water boiling point was defined to be 212oF
fallow
a farming technique in which arable land is left without replanting during a planting season
fault
crack in the Earth's crust often associated with boundaries between Earth's tectonic plates
fauna
the animals of a particular region, habitat, or geological period


 fluvial
of or found in a river
fluvioglacial
relating to erosion or deposition caused by flowing meltwater from glaciers or ice sheets
fog
a thick cloud of tiny water droplets suspended in the atmosphere near Earth's surface
fold
when originally flat, level surfaces, such as sedimentary strata, are bent or curved as a result of pressure and high temperature
foliated
the parallel arrangement of certain mineral grains that gives the rock a striped appearance
forage crop
grown specifically to be grazed by livestock or conserved as hay or silage
forcing
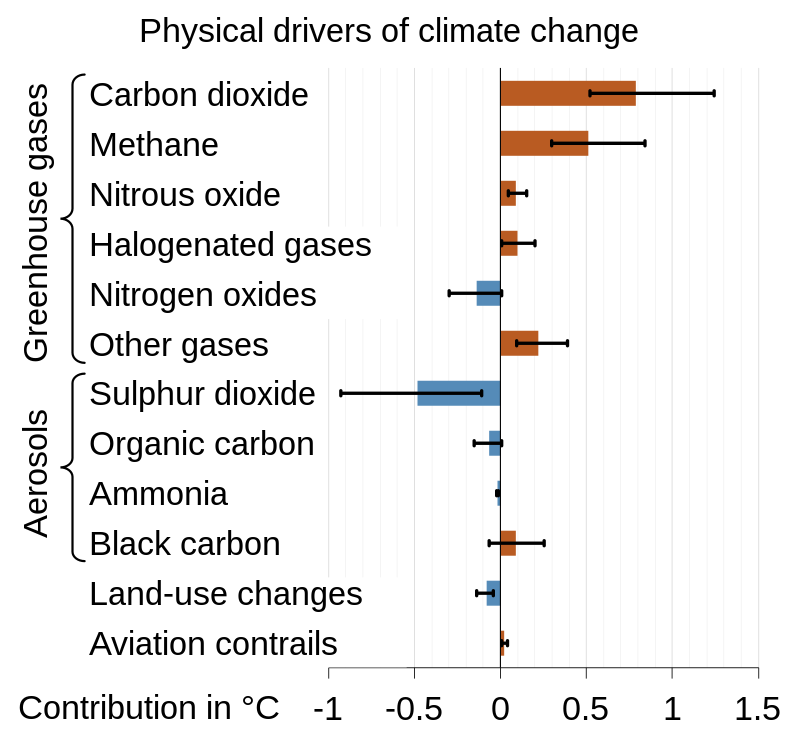
initial climate drivers, including solar irradiance, greenhous gas emissions, and airborne particles like dust, smoke, and soot that come from both human and natural sources
fossiliferous
refers to rock containing many fossils
freshet
flood of a river from heavy rain or melted snow
fresh water
characterized by having low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids
fluvial
of or found in a river
fluvioglacial
relating to erosion or deposition caused by flowing meltwater from glaciers or ice sheets
fog
a thick cloud of tiny water droplets suspended in the atmosphere near Earth's surface
fold
when originally flat, level surfaces, such as sedimentary strata, are bent or curved as a result of pressure and high temperature
foliated
the parallel arrangement of certain mineral grains that gives the rock a striped appearance
forage crop
grown specifically to be grazed by livestock or conserved as hay or silage
forcing
initial climate drivers, including solar irradiance, greenhous gas emissions, and airborne particles like dust, smoke, and soot that come from both human and natural sources
fossiliferous
refers to rock containing many fossils
freshet
flood of a river from heavy rain or melted snow
fresh water
characterized by having low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids


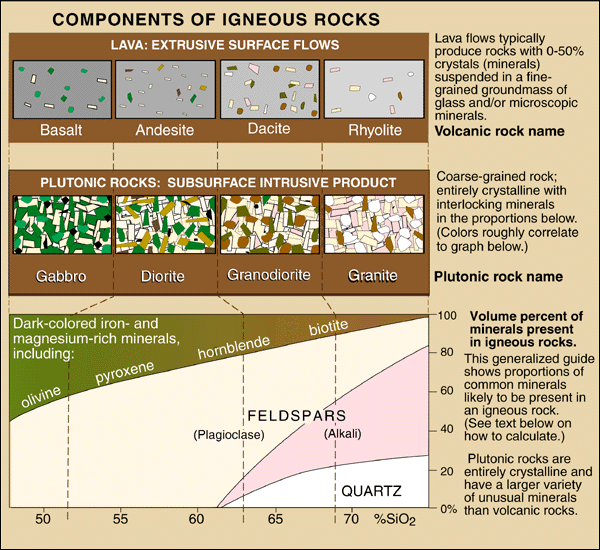
 gabbro
a dense, mafic intrusive rock generally occurring as batholiths and laccoliths and often found along mid-ocean ridges or in ancient mountains composed
of compressed and uplifted oceanic crust
gage height
the height of water measured by a water gage
gaging station
a site on a flowing water body where hydrologic data is obtained
gale
a very strong wind
garnet
a large group of rock-forming minerals with a common crystal structure, (X3Y2(SiO4)3)
gated pipe system
a surface pipe that is usually polyvinyl chloride or aluminum fitted with spaced closeable gates or holes permitting the water to flow into furrows, borders or basins
gene
the basic physical and functional unit of heredity
general adjudication
an action for judicial determination
general industrial use permit
permits for the withdrawal of groundwater outside the boundaries of a service area
general stream adjudication
a state court proceeding to resolve disputes over water priorities and competing uses across an entire river basin
genetics
the study of heredity and the variation of inherited characteristics
genotoxicity
refers to substances bind to DNA and causing genetic mutations which can cause cancer and birth defects
geochronology
the branch of geology concerned with the dating of rock formations and geological events
geodetic
relating to land surveying
geogenic
relating to the Earth
gabbro
a dense, mafic intrusive rock generally occurring as batholiths and laccoliths and often found along mid-ocean ridges or in ancient mountains composed
of compressed and uplifted oceanic crust
gage height
the height of water measured by a water gage
gaging station
a site on a flowing water body where hydrologic data is obtained
gale
a very strong wind
garnet
a large group of rock-forming minerals with a common crystal structure, (X3Y2(SiO4)3)
gated pipe system
a surface pipe that is usually polyvinyl chloride or aluminum fitted with spaced closeable gates or holes permitting the water to flow into furrows, borders or basins
gene
the basic physical and functional unit of heredity
general adjudication
an action for judicial determination
general industrial use permit
permits for the withdrawal of groundwater outside the boundaries of a service area
general stream adjudication
a state court proceeding to resolve disputes over water priorities and competing uses across an entire river basin
genetics
the study of heredity and the variation of inherited characteristics
genotoxicity
refers to substances bind to DNA and causing genetic mutations which can cause cancer and birth defects
geochronology
the branch of geology concerned with the dating of rock formations and geological events
geodetic
relating to land surveying
geogenic
relating to the Earth
 geographic coordinate system
a spherical coordinate system for measuring and communicating positions using latitude and longitude
geographic north pole
the point in the Northern Hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface
geologic province
a geologic area with common geologic attributes
geologic time scale
a system of chronological dating that classifies geological strata by time
geology
the science that deals with Earth's physical structure and substance, its history, and the processes that act on it
geomagnetic reversal
when a planet's magnetic north and magnetic south switch positions
geyser
a hot spring in which water intermittently boils, and emits a tall column of water and steam into the atmosphere
giardia
a tiny parasite that causes the diarrhea
gigawatt (GW)
a unit of electric power equal to one billion watts
gigawatt hour (GWh)
a unit of energy representing one billion watt hours
glacial lake
a body of water with origins from glacier activity
glacial lake outburst flood (GLOF)
a flood caused by the failure of a dam containing a glacial lake
geographic coordinate system
a spherical coordinate system for measuring and communicating positions using latitude and longitude
geographic north pole
the point in the Northern Hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface
geologic province
a geologic area with common geologic attributes
geologic time scale
a system of chronological dating that classifies geological strata by time
geology
the science that deals with Earth's physical structure and substance, its history, and the processes that act on it
geomagnetic reversal
when a planet's magnetic north and magnetic south switch positions
geyser
a hot spring in which water intermittently boils, and emits a tall column of water and steam into the atmosphere
giardia
a tiny parasite that causes the diarrhea
gigawatt (GW)
a unit of electric power equal to one billion watts
gigawatt hour (GWh)
a unit of energy representing one billion watt hours
glacial lake
a body of water with origins from glacier activity
glacial lake outburst flood (GLOF)
a flood caused by the failure of a dam containing a glacial lake
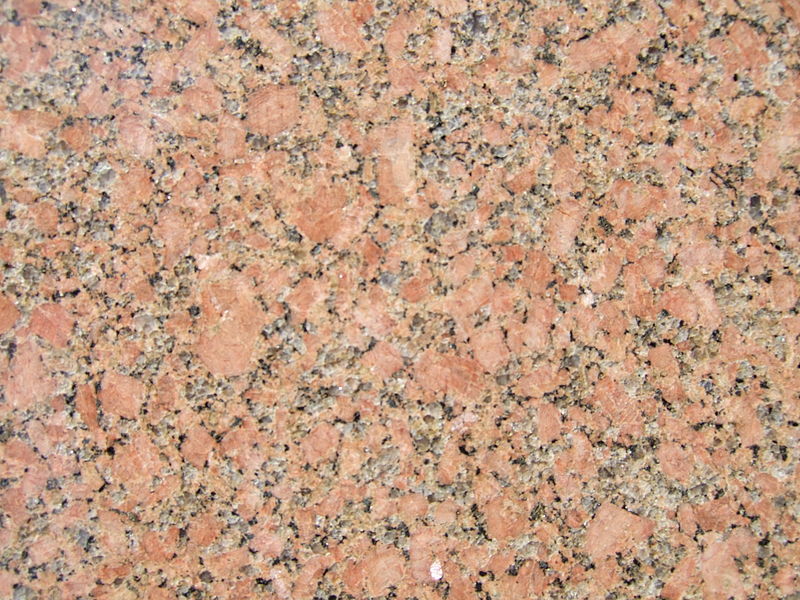


 granite
formed from the slow crystallization of magma below Earth's surface, a light-colored igneous rock composed mainly of quartz and feldspar with minor amounts of
mica, amphiboles, and other minerals with grains large enough to be visible with the unaided eye
granular activated carbon (GAC)
materials that absorb thousands of organic and some inorganic materials
graupel
precipitation that forms when supercooled water droplets are collected and freeze on falling snowflakes, forming 2 to 5 millimeter balls of rime
gravel
loose aggregation of rock fragments, classified by particle size range and includes size classes from granule- to boulder-sized fragments
gravimeter
a device for measuring Earth's gravitational field variations
gravity
the force that draws objects toward the center of planets, moons, stars or other bodies
gravity flow irrigation
irrigation in which the water flows under gravity from the source to the field
gray infrastructure
systems of gutters, pipes and tunnels that move stormwater to treatment plants or to local water bodies
Great Pacific garbage patch
a collection of plastic and floating trash in the central North Pacific Ocean originating from the Pacific Rim, including countries in Asia, North America and South America
granite
formed from the slow crystallization of magma below Earth's surface, a light-colored igneous rock composed mainly of quartz and feldspar with minor amounts of
mica, amphiboles, and other minerals with grains large enough to be visible with the unaided eye
granular activated carbon (GAC)
materials that absorb thousands of organic and some inorganic materials
graupel
precipitation that forms when supercooled water droplets are collected and freeze on falling snowflakes, forming 2 to 5 millimeter balls of rime
gravel
loose aggregation of rock fragments, classified by particle size range and includes size classes from granule- to boulder-sized fragments
gravimeter
a device for measuring Earth's gravitational field variations
gravity
the force that draws objects toward the center of planets, moons, stars or other bodies
gravity flow irrigation
irrigation in which the water flows under gravity from the source to the field
gray infrastructure
systems of gutters, pipes and tunnels that move stormwater to treatment plants or to local water bodies
Great Pacific garbage patch
a collection of plastic and floating trash in the central North Pacific Ocean originating from the Pacific Rim, including countries in Asia, North America and South America

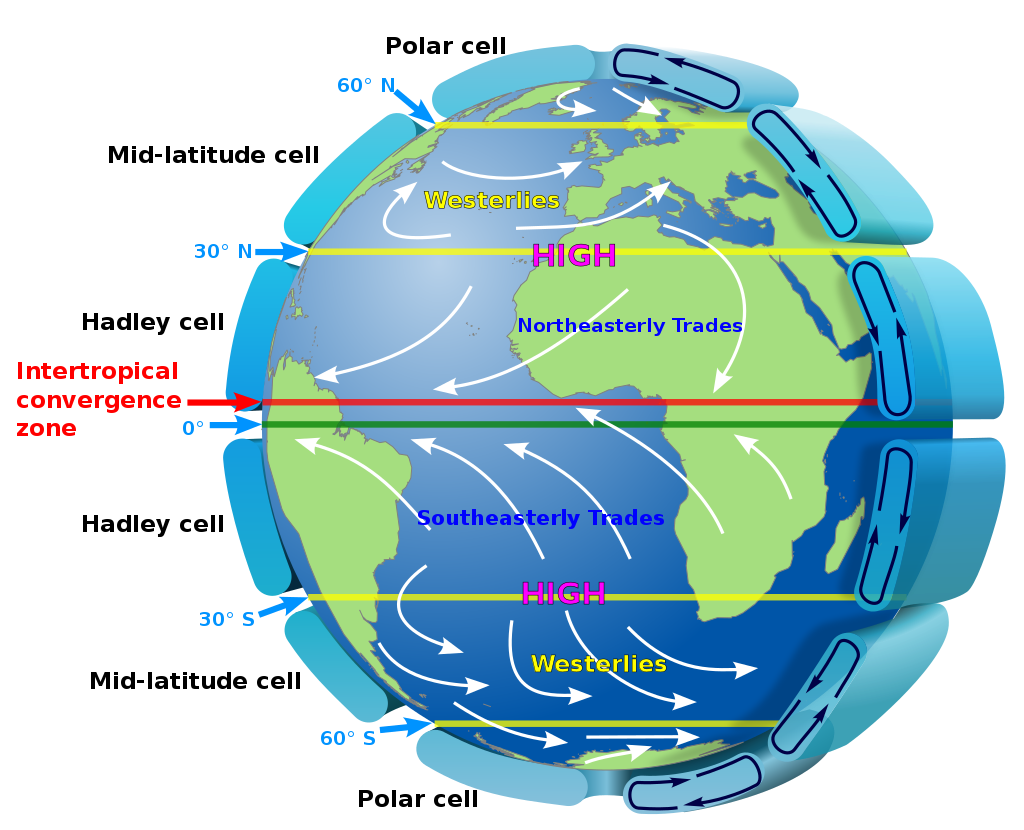
 Hadley cell
global tropical atmospheric circulation where air rises near the Equator, flows poleward, descending in the subtropics and then returns toward the equator near Earth's surface
hadopelagic zone
where deep, wide trenches occur in the flat seafloor
hail
a form of precipitation made when supercooled water droplets freeze on contact with dust or dirt
halide
contain the element chlorine ionically bonded with sodium or other cations
halogen
the reactive nonmetallic elements fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine, occupying group VIIA of the periodic table that form strongly acidic compounds with hydrogen from which simple salts can be made
halophyte
a plant adapted to growing in salty conditions
hanging glacier
a glacier that begins high on a glacier valley wall and descends only part of the way to the surface of the main glacier
hanging valley
a valley cut across by a deeper valley or a cliff
hardness
refers to the concentration of calcium and magnesium in water
hardpan
a hard layer of clay below soil that prevents drainage and plant growth
Hadley cell
global tropical atmospheric circulation where air rises near the Equator, flows poleward, descending in the subtropics and then returns toward the equator near Earth's surface
hadopelagic zone
where deep, wide trenches occur in the flat seafloor
hail
a form of precipitation made when supercooled water droplets freeze on contact with dust or dirt
halide
contain the element chlorine ionically bonded with sodium or other cations
halogen
the reactive nonmetallic elements fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine, occupying group VIIA of the periodic table that form strongly acidic compounds with hydrogen from which simple salts can be made
halophyte
a plant adapted to growing in salty conditions
hanging glacier
a glacier that begins high on a glacier valley wall and descends only part of the way to the surface of the main glacier
hanging valley
a valley cut across by a deeper valley or a cliff
hardness
refers to the concentration of calcium and magnesium in water
hardpan
a hard layer of clay below soil that prevents drainage and plant growth

 headwater
the source of a stream or river
heap and dump leaching
mineral extraction using acid solutions applied to metallic ores
heat index
a measure indicating an average person's discomfort level experienced as a result of combined effects of air temperature and humidity
heavy water
water that contains more than a normal amount of the hydrogen isotope deuterium
hectare
a metric unit of square measure, equal to 2.471 acres or 10,000 square meters
helictite
a distorted form of stalactite that resembles a twig
hematite
a common iron oxide black to steel or silver-gray, brown to reddish-brown, or red in color that usually precipitates from water and collect in layers at the bottom of a lake, spring, or other standing water
hemiacetal hydroxyl group
a functional group with the chemical formula -OH and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom
hepatitis A
a highly contagious liver infection caused by the hepatitis A virus
herbicide
a substance that is toxic to plants
headwater
the source of a stream or river
heap and dump leaching
mineral extraction using acid solutions applied to metallic ores
heat index
a measure indicating an average person's discomfort level experienced as a result of combined effects of air temperature and humidity
heavy water
water that contains more than a normal amount of the hydrogen isotope deuterium
hectare
a metric unit of square measure, equal to 2.471 acres or 10,000 square meters
helictite
a distorted form of stalactite that resembles a twig
hematite
a common iron oxide black to steel or silver-gray, brown to reddish-brown, or red in color that usually precipitates from water and collect in layers at the bottom of a lake, spring, or other standing water
hemiacetal hydroxyl group
a functional group with the chemical formula -OH and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom
hepatitis A
a highly contagious liver infection caused by the hepatitis A virus
herbicide
a substance that is toxic to plants

 heterogeneous
relating to substances in different phases or composed of different materials
heterotrophic
refers to an organism deriving its nutritional requirements from complex organic substances
hexafluoroethane
a non-flammable, long-lived greenhouse gas negligibly soluble in water and slightly soluble in alcohol
high seas
open ocean that begins 200 nautical miles from a coastline and is not under the jurisdiction of the laws of any specific country
homogeneous
of uniform structure or composition
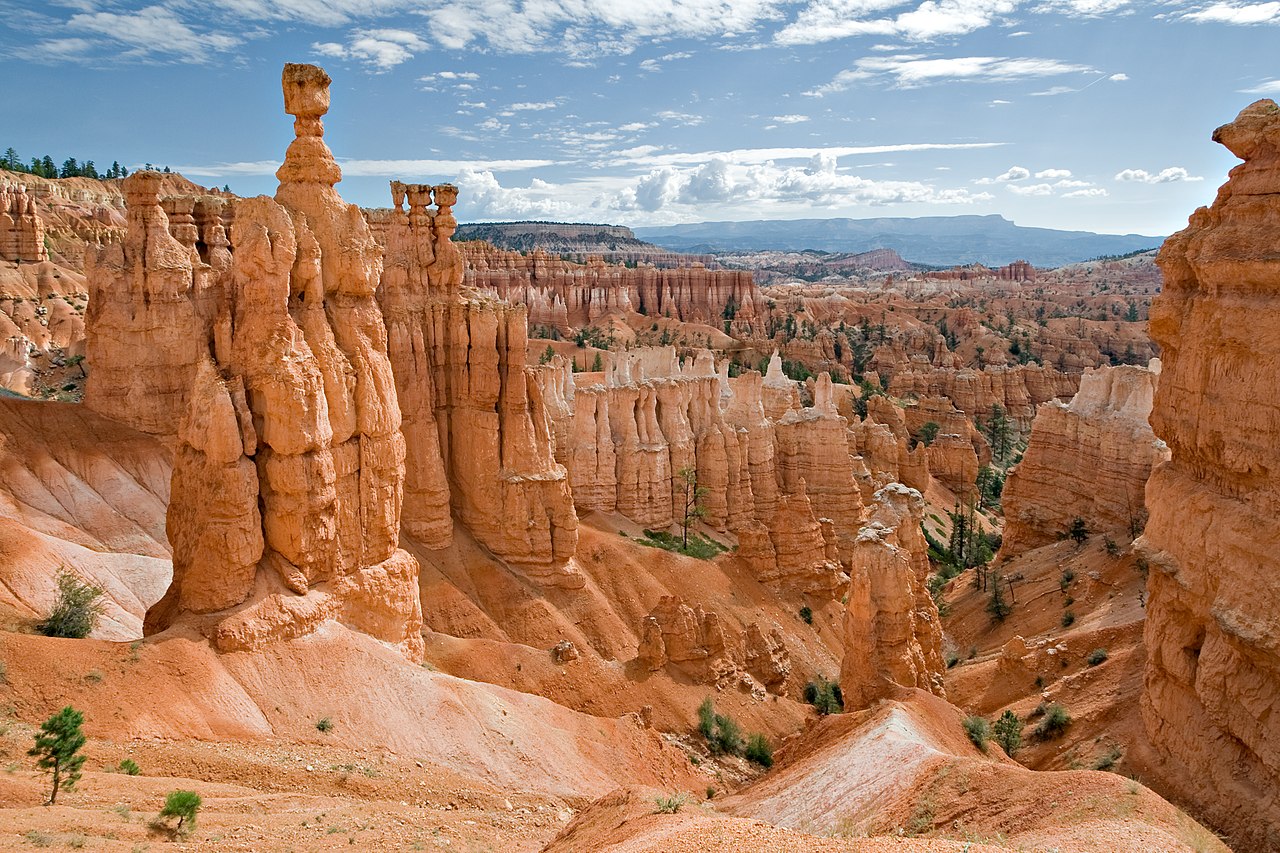
hoodoo
a column or pinnacle of weathered rock
hornblende
a dark brown, black, or green mineral of the amphibole group consisting of a hydroxyl alumino-silicate of calcium, magnesium, and iron, occurring
in many igneous and metamorphic rocks
hornfels
a metamorphic rock formed by the contact between mudstone and shale, or other clay-rich rock, and a hot igneous body,
representing a heat-altered equivalent of the original rock
heterogeneous
relating to substances in different phases or composed of different materials
heterotrophic
refers to an organism deriving its nutritional requirements from complex organic substances
hexafluoroethane
a non-flammable, long-lived greenhouse gas negligibly soluble in water and slightly soluble in alcohol
high seas
open ocean that begins 200 nautical miles from a coastline and is not under the jurisdiction of the laws of any specific country
homogeneous
of uniform structure or composition
hoodoo
a column or pinnacle of weathered rock
hornblende
a dark brown, black, or green mineral of the amphibole group consisting of a hydroxyl alumino-silicate of calcium, magnesium, and iron, occurring
in many igneous and metamorphic rocks
hornfels
a metamorphic rock formed by the contact between mudstone and shale, or other clay-rich rock, and a hot igneous body,
representing a heat-altered equivalent of the original rock

 horse latitudes
located at about 30 degrees north and south of the equator, an area of divergent winds that flow toward the poles or toward the equator due to high pressure resulting in calm winds, sunny skies and little or no precipitation
hot desert
a desert with average temperatures above 30C and a day time temperature often higher than 50oC
hotspot
volcanic regions that are not found at the edges of continents or faults
household water security
safe and reliable access to sufficient quantity and quality of water for household consumption, production and cleanliness
humidity
concentration of water vapor present in the air
humus
the organic component of soil, formed by the decomposition of leaves and other plant material by soil microorganisms
hurricane
storm with a violent wind, in particular a tropical cyclone in the Caribbean
hydration
process of combining a substance with water molecules
hydraulic
relating to or operated by a liquid moving in a confined space under pressure
hydraulic conductivity
the rate of flow of water through a unit cross sectional area of an aquifer
What is Earth`s albedo?
hydraulic gradient
the difference between two hydraulic head measurements divided by the distance between the two measurements
hydraulic head
a specific measurement of liquid pressure above at a defined vertical height
hydraulic radius
the area of the flow section divided by the wetted perimeter
hydraulic retention time (HRT)
the ratio between the reactor volume and the feed flow rate, represents the average time the cells and substrates stay inside the reactor
hydroelectric power
the use of flowing water to power a turbine to produce electrical energy
hydrogel
a gel in which the liquid component is water
hydrogen sulfide
gaseous substance found in several inorganic water pollutant such as electric power waste, oil and gas extraction operations waste,
sewage treatment plants, large pig farms and other confined animal feeding operations, Portland cement kilns, municipal waste landfills, coke ovens,
sulfur products, asphalt production and storage and geothermal power plants, (H2S)
horse latitudes
located at about 30 degrees north and south of the equator, an area of divergent winds that flow toward the poles or toward the equator due to high pressure resulting in calm winds, sunny skies and little or no precipitation
hot desert
a desert with average temperatures above 30C and a day time temperature often higher than 50oC
hotspot
volcanic regions that are not found at the edges of continents or faults
household water security
safe and reliable access to sufficient quantity and quality of water for household consumption, production and cleanliness
humidity
concentration of water vapor present in the air
humus
the organic component of soil, formed by the decomposition of leaves and other plant material by soil microorganisms
hurricane
storm with a violent wind, in particular a tropical cyclone in the Caribbean
hydration
process of combining a substance with water molecules
hydraulic
relating to or operated by a liquid moving in a confined space under pressure
hydraulic conductivity
the rate of flow of water through a unit cross sectional area of an aquifer
What is Earth`s albedo?
hydraulic gradient
the difference between two hydraulic head measurements divided by the distance between the two measurements
hydraulic head
a specific measurement of liquid pressure above at a defined vertical height
hydraulic radius
the area of the flow section divided by the wetted perimeter
hydraulic retention time (HRT)
the ratio between the reactor volume and the feed flow rate, represents the average time the cells and substrates stay inside the reactor
hydroelectric power
the use of flowing water to power a turbine to produce electrical energy
hydrogel
a gel in which the liquid component is water
hydrogen sulfide
gaseous substance found in several inorganic water pollutant such as electric power waste, oil and gas extraction operations waste,
sewage treatment plants, large pig farms and other confined animal feeding operations, Portland cement kilns, municipal waste landfills, coke ovens,
sulfur products, asphalt production and storage and geothermal power plants, (H2S)





 laccolith
a lens-shaped mass of igneous rock, that has been intruded between rock strata causing a dome-shaped uplift
lacustrine
related to lakes
lagoon
shallow body of water separated from a larger body of water by a reef, barrier island, barrier peninsula or isthmus
lake
a body of water in which surface water is accumulated
lamella
refers to clarifiers used in municipal water and wastewater treatment and industrial applications
La Niña
an oceanic and atmospheric phenomenon that is the colder counterpart of El Niño
land breeze
a night breeze created due to faster land cooling than ocean cooling
lapse rate
rate at which an atmospheric temperature decreases with increasing altitude
large community water system
a community water system that serves more than 1,850 acre-feet of water
large municipal provider
a municipal water provider that serves more than 250 acre-feet of water for non-irrigation purposes during a calendar year
laccolith
a lens-shaped mass of igneous rock, that has been intruded between rock strata causing a dome-shaped uplift
lacustrine
related to lakes
lagoon
shallow body of water separated from a larger body of water by a reef, barrier island, barrier peninsula or isthmus
lake
a body of water in which surface water is accumulated
lamella
refers to clarifiers used in municipal water and wastewater treatment and industrial applications
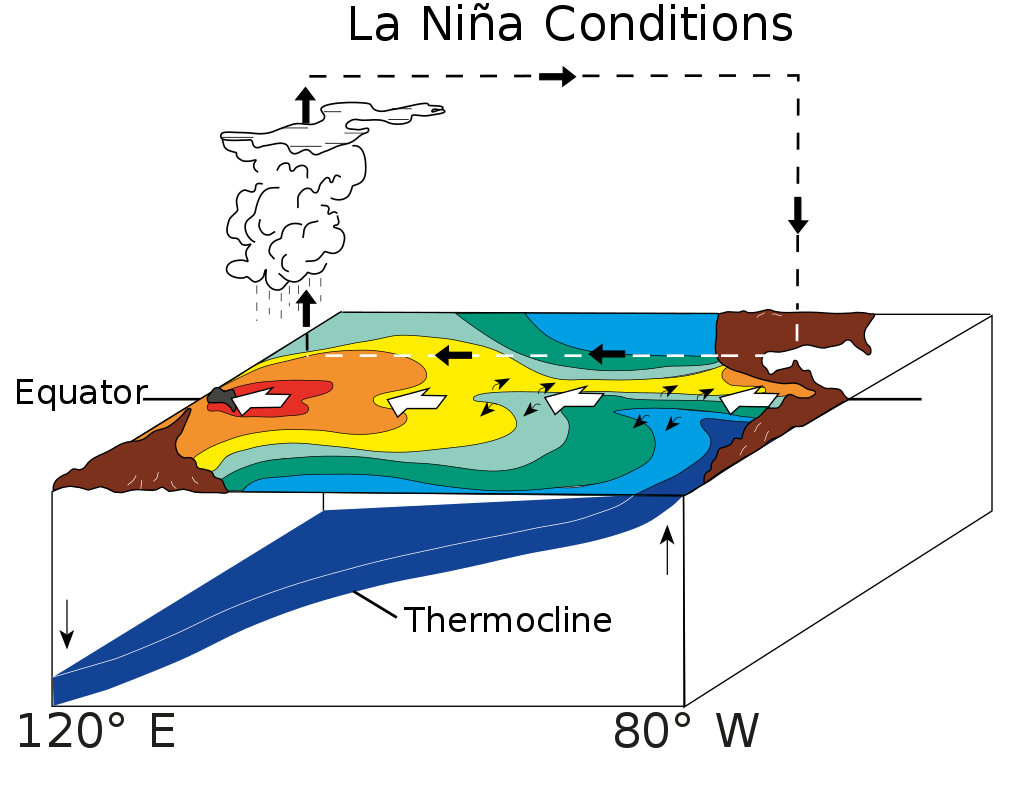
La Niña
an oceanic and atmospheric phenomenon that is the colder counterpart of El Niño
land breeze
a night breeze created due to faster land cooling than ocean cooling
lapse rate
rate at which an atmospheric temperature decreases with increasing altitude
large community water system
a community water system that serves more than 1,850 acre-feet of water
large municipal provider
a municipal water provider that serves more than 250 acre-feet of water for non-irrigation purposes during a calendar year

 leach
drain away from soil, ash or other material by water
lead
a soft, dense, malleable metal with a relatively low melting point
lentic water
refers to standing water in ponds or lakes
lepidolite
a lilac-gray or rose-colored member of the mica group of minerals
leptospirosis
an infectious bacterial disease that occurs in rodents, dogs, and other mammals and can be transmitted to humans
levee
an earthen barrier along a stream, lake or river that protects the surrounding land from flooding
lime
a white caustic alkaline substance consisting of calcium oxide, which is obtained by heating limestone and which combines with water with the production of much hea
limestone
hard sedimentary rock, composed mainly of calcium carbonate or dolomite, used as building material and in the making of cement
leach
drain away from soil, ash or other material by water
lead
a soft, dense, malleable metal with a relatively low melting point
lentic water
refers to standing water in ponds or lakes
lepidolite
a lilac-gray or rose-colored member of the mica group of minerals
leptospirosis
an infectious bacterial disease that occurs in rodents, dogs, and other mammals and can be transmitted to humans
levee
an earthen barrier along a stream, lake or river that protects the surrounding land from flooding
lime
a white caustic alkaline substance consisting of calcium oxide, which is obtained by heating limestone and which combines with water with the production of much hea
limestone
hard sedimentary rock, composed mainly of calcium carbonate or dolomite, used as building material and in the making of cement

 limitrophe
situated on a border or frontier
limnology
study of fresh waters, specifically those found in lakes and ponds
Linnaean taxonomy
a classification system that groups organisms based on commonalities by domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus and species
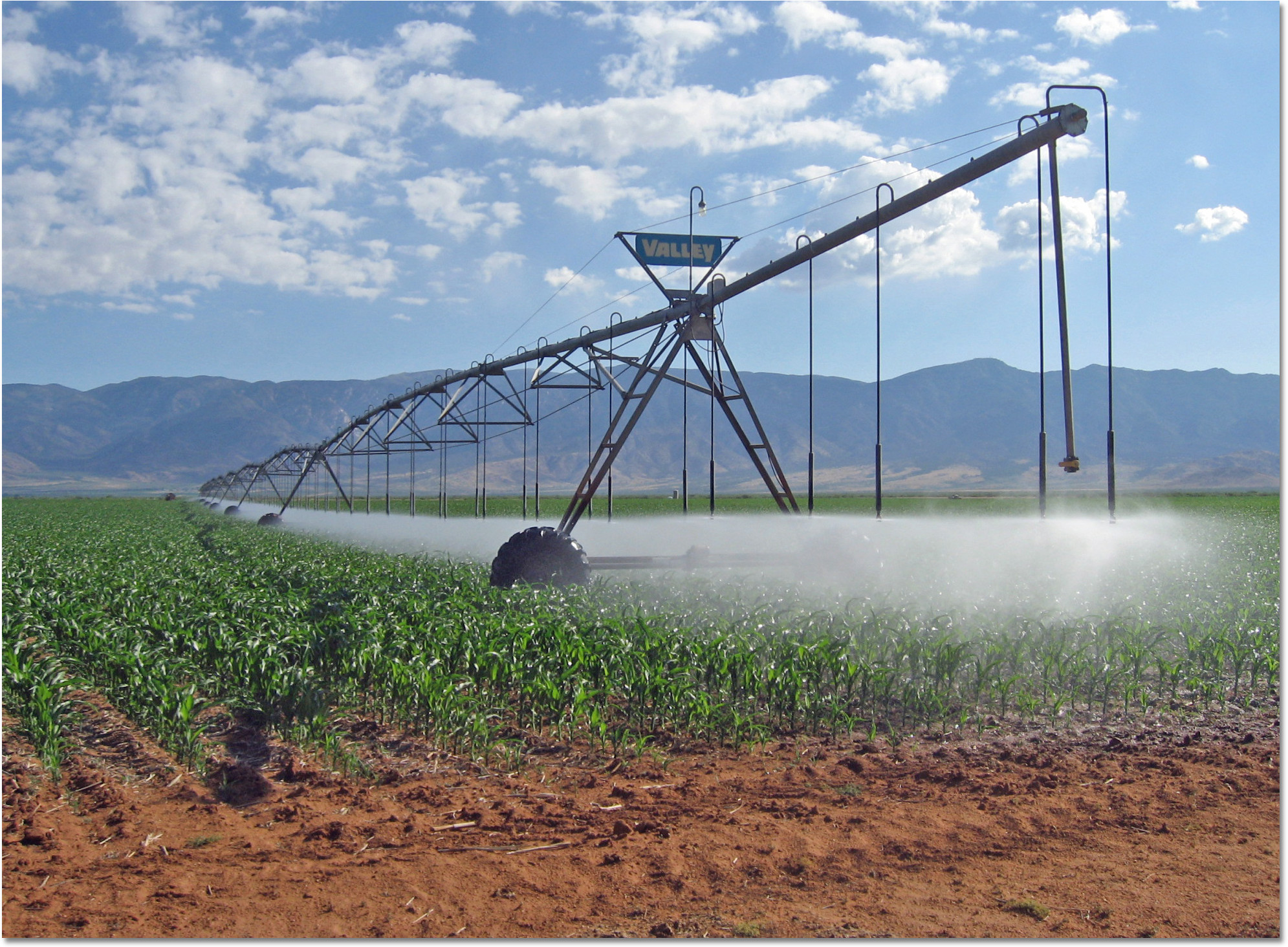
linear move tower system
a self-propelled continuous move side-roll system on a tower, a center pivot system adapted to move in a line and designed for use on square fields,
ater is supplied to the unit by a flexible rubber hose
listric fault
similar to a normal fault but the fault plane curves with the dip being steeper near the surface and shallower with increased depth
lithify
transform from sediment into stone
lithology
study of rocks
lithosphere
the rigid outer part of the Earth, consisting of the crust and upper mantle
Little Ice Age
climate cooling period that occurred from the early 14th century through the mid-19th century, when mountain glaciers expanded at several locations, including the European Alps, New Zealand, Alaska, and the southern Andes, and mean annual temperatures across the Northern Hemisphere declined by 0.6oC
limitrophe
situated on a border or frontier
limnology
study of fresh waters, specifically those found in lakes and ponds
Linnaean taxonomy
a classification system that groups organisms based on commonalities by domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus and species
linear move tower system
a self-propelled continuous move side-roll system on a tower, a center pivot system adapted to move in a line and designed for use on square fields,
ater is supplied to the unit by a flexible rubber hose
listric fault
similar to a normal fault but the fault plane curves with the dip being steeper near the surface and shallower with increased depth
lithify
transform from sediment into stone
lithology
study of rocks
lithosphere
the rigid outer part of the Earth, consisting of the crust and upper mantle
Little Ice Age
climate cooling period that occurred from the early 14th century through the mid-19th century, when mountain glaciers expanded at several locations, including the European Alps, New Zealand, Alaska, and the southern Andes, and mean annual temperatures across the Northern Hemisphere declined by 0.6oC


 meridian
a line of longitude
mesa
an isolated flat-topped hill with steep sides, found in landscapes with horizontal strata
mesopelagic zone
middle open ocean, from the bottom of the epipelagic to the point where sunlight can't reach, approximately 1000 m (3300 feet) deep
mesosphere
Earth's third atmospheric layer, above the stratosphere and below the thermosphere and where temperature decreases as altitude increases
Mesozoic
relating to or denoting the era between the Paleozoic and Cenozoic eras, comprising the Triassic, Jurassic, and Cretaceous periods
metabolism
chemical processes in a living organism that keep it alive
metalimnion
the middle layer of water in a stratified lake characterized by a rapid change in temperature with depth
metalocene
tiny particle of positively charged metal ions between two rings of carbon atoms which each have five atoms
meridian
a line of longitude
mesa
an isolated flat-topped hill with steep sides, found in landscapes with horizontal strata
mesopelagic zone
middle open ocean, from the bottom of the epipelagic to the point where sunlight can't reach, approximately 1000 m (3300 feet) deep
mesosphere
Earth's third atmospheric layer, above the stratosphere and below the thermosphere and where temperature decreases as altitude increases
Mesozoic
relating to or denoting the era between the Paleozoic and Cenozoic eras, comprising the Triassic, Jurassic, and Cretaceous periods
metabolism
chemical processes in a living organism that keep it alive
metalimnion
the middle layer of water in a stratified lake characterized by a rapid change in temperature with depth
metalocene
tiny particle of positively charged metal ions between two rings of carbon atoms which each have five atoms

 metal-organic frameworks (MOF)
crystalline compounds consisting of rigid, porous organic molecules
metamorphic
relating to rock that has undergone transformation by heat, pressure, or other natural processes
meteorology
the branch of science concerned with the processes and phenomena of the atmosphere, especially as a means of forecasting the weather
methane
a powerful greenhouse gas and the simplest hydrocarbon, consisting of one carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms, (CH4)
method detection limit (MDL)
the minimum measured concentration of a substance that can be reported with 99% confidence that the measured concentration is distinguishable
from method blank results
method reporting limit (MRL)
the minimum concentration of a contaminant reported after analyzing a sample, determined after corrections have been made for sample dilution and sample weight
mgd
million gallons per day
mica
a shiny silicate mineral with a layered structure, found as minute scales in granite and other rocks, or as crystals
metal-organic frameworks (MOF)
crystalline compounds consisting of rigid, porous organic molecules
metamorphic
relating to rock that has undergone transformation by heat, pressure, or other natural processes
meteorology
the branch of science concerned with the processes and phenomena of the atmosphere, especially as a means of forecasting the weather
methane
a powerful greenhouse gas and the simplest hydrocarbon, consisting of one carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms, (CH4)
method detection limit (MDL)
the minimum measured concentration of a substance that can be reported with 99% confidence that the measured concentration is distinguishable
from method blank results
method reporting limit (MRL)
the minimum concentration of a contaminant reported after analyzing a sample, determined after corrections have been made for sample dilution and sample weight
mgd
million gallons per day
mica
a shiny silicate mineral with a layered structure, found as minute scales in granite and other rocks, or as crystals

 microatoll
community of species of corals where vertical growth limited by average tidal height
microclimate
a local set of atmospheric conditions that differ from those in the surrounding areas
microfiltration
contaminated fluid is passed through a filter to remove microorganisms and suspended particles
microplastics
invisible pieces of plastic measuring less than 5 millimeters
micro-sprinkler system
supplies water through emitters and nozzles attached to a supply pipe or porous tubing
microwave
an electromagnetic wave with a wavelength in the range 0.001 and 0.3 m, shorter than a radio wave and longer than infrared radiation
migmatite
a composite rock found in medium and high-grade metamorphic environments
mineral
substance occurring in nature usually comprising inorganic materials of definite chemical composition and definite crystal structure,
may include organic substances such as coal
minimum detectable concentration (MDC)
the net concentration that has a specified chance of being detected, an estimate of the detection capability of a measuring system
mining use
water used for quarrying and mineral extraction
minute
an official record of what was said and done in a meeting
miscible
forming a homogeneous mixture when added together
mitigation
actions taken to reduce the seriousness of something
microatoll
community of species of corals where vertical growth limited by average tidal height
microclimate
a local set of atmospheric conditions that differ from those in the surrounding areas
microfiltration
contaminated fluid is passed through a filter to remove microorganisms and suspended particles
microplastics
invisible pieces of plastic measuring less than 5 millimeters
micro-sprinkler system
supplies water through emitters and nozzles attached to a supply pipe or porous tubing
microwave
an electromagnetic wave with a wavelength in the range 0.001 and 0.3 m, shorter than a radio wave and longer than infrared radiation
migmatite
a composite rock found in medium and high-grade metamorphic environments
mineral
substance occurring in nature usually comprising inorganic materials of definite chemical composition and definite crystal structure,
may include organic substances such as coal
minimum detectable concentration (MDC)
the net concentration that has a specified chance of being detected, an estimate of the detection capability of a measuring system
mining use
water used for quarrying and mineral extraction
minute
an official record of what was said and done in a meeting
miscible
forming a homogeneous mixture when added together
mitigation
actions taken to reduce the seriousness of something
 mixed liquor suspended solids
concentration of suspended solids, in an aeration tank during the activated sludge process, which occurs during the treatment of waste water
mixed liquor volatile suspended solids (MLVSS)
the amount of organic or volatile suspended solids in the mixed liquor of an aeration tank, used as a measure or indication of the microorganisms present
mld
megaliters per day
Mohorovičić discontinuity
the boundary between the Earth's crust and the mantle, also called the Moho
Mohs hardness scale
scale used to classify a mineral's hardness
molecular polarity
a separation of electric charge in a molecule that results in a negatively charged end and a positively charged end
molecule
a group of atoms bonded together, representing the smallest fundamental unit of a chemical compound that can take part in a chemical reaction
mixed liquor suspended solids
concentration of suspended solids, in an aeration tank during the activated sludge process, which occurs during the treatment of waste water
mixed liquor volatile suspended solids (MLVSS)
the amount of organic or volatile suspended solids in the mixed liquor of an aeration tank, used as a measure or indication of the microorganisms present
mld
megaliters per day
Mohorovičić discontinuity
the boundary between the Earth's crust and the mantle, also called the Moho
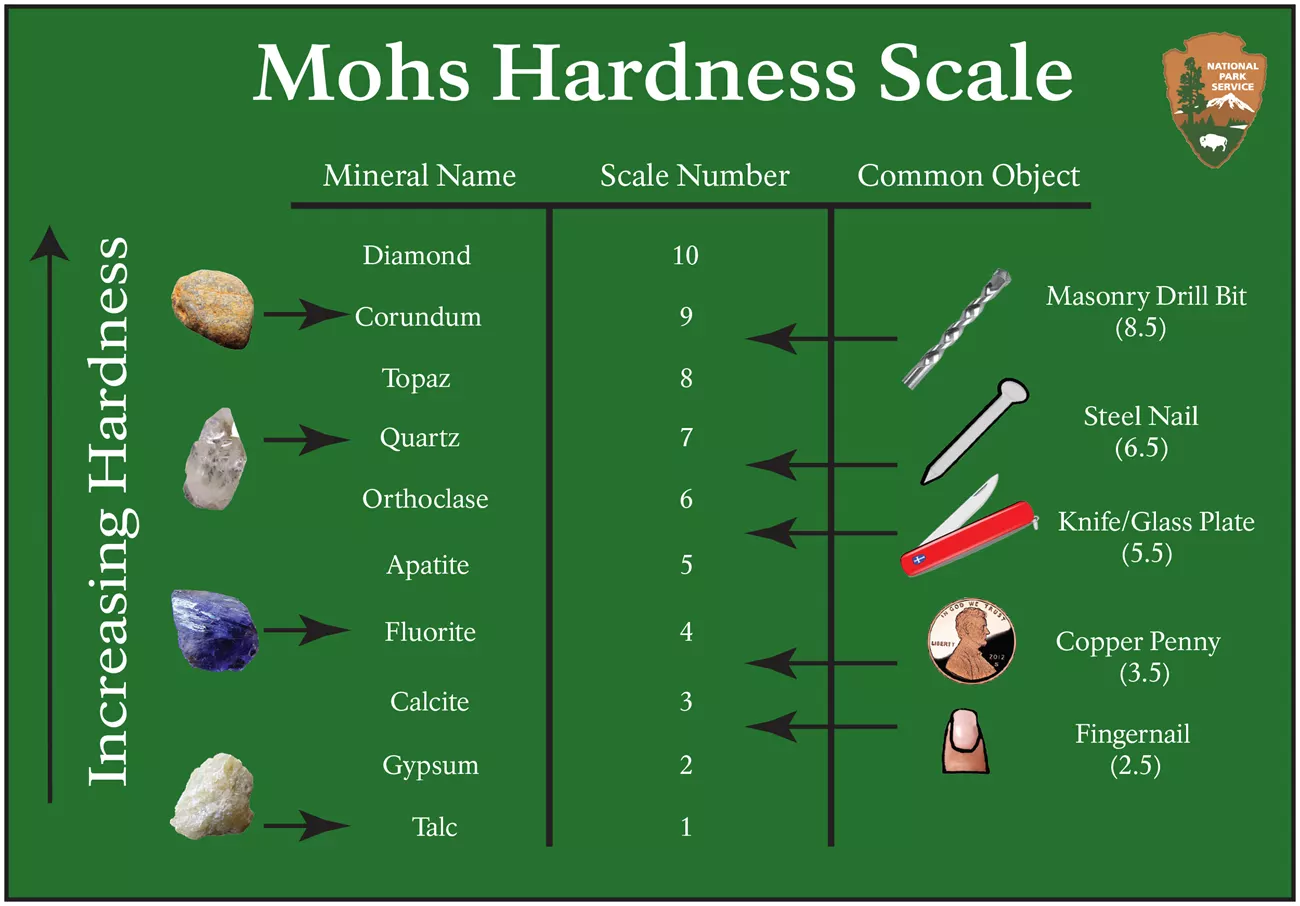
Mohs hardness scale
scale used to classify a mineral's hardness
molecular polarity
a separation of electric charge in a molecule that results in a negatively charged end and a positively charged end
molecule
a group of atoms bonded together, representing the smallest fundamental unit of a chemical compound that can take part in a chemical reaction
 monadnock
an isolated hill or ridge of erosion-resistant rock rising above a peneplain
monitor well
a well designed and drilled for monitoring purposes
monoclinal ridge
top of a step-like fold in rock strata consisting of a zone of steeper dip within an otherwise horizontal or gently-dipping sequence
monocline
a bend in rock strata that are otherwise uniformly dipping or horizontal
monsoon
a seasonal change in prevailing wind direction that often results in weeks or months of rainy weather
montmorillonite
an aluminum-rich clay mineral of the smectite group containing some sodium and magnesium
monzonite
a granular igneous rock with a composition between syenite and diorite, containing equal amounts of orthoclase and plagioclase
monadnock
an isolated hill or ridge of erosion-resistant rock rising above a peneplain
monitor well
a well designed and drilled for monitoring purposes
monoclinal ridge
top of a step-like fold in rock strata consisting of a zone of steeper dip within an otherwise horizontal or gently-dipping sequence
monocline
a bend in rock strata that are otherwise uniformly dipping or horizontal
monsoon
a seasonal change in prevailing wind direction that often results in weeks or months of rainy weather
montmorillonite
an aluminum-rich clay mineral of the smectite group containing some sodium and magnesium
monzonite
a granular igneous rock with a composition between syenite and diorite, containing equal amounts of orthoclase and plagioclase


 nanofiltration (NF)
a membrane liquid-separation technology that removes multivalent ions
native element
occurs in nature in a nearly pure state, metals include platinum, iridium, osmium, iron, zinc, tin, gold, silver, copper, mercury, lead and chromium, semimetals include bismuth, antimony, arsenic, tellurium and selenium and nonmetals include sulfur and carbon
natural satellite
an astronomical body that orbits a planet, dwarf planet or small solar system body, often called a moon
nautical mile
unit used in measuring distances at sea equal to approximately 2,025 yards or 1,852 meters
navigable waters
waters that are subject to tidal action and those that may be used for interstate or foreign commerce
neap tide
a tide just after the first or third quarters of the Moon when there is least difference between high and low water
negative environmental feedback loop
an environmental process that diminishes the effect of climate forcing
neopelagic
refers to a marine environment in the Great Garbage Patch were open-ocean and coastal species live together
nanofiltration (NF)
a membrane liquid-separation technology that removes multivalent ions
native element
occurs in nature in a nearly pure state, metals include platinum, iridium, osmium, iron, zinc, tin, gold, silver, copper, mercury, lead and chromium, semimetals include bismuth, antimony, arsenic, tellurium and selenium and nonmetals include sulfur and carbon
natural satellite
an astronomical body that orbits a planet, dwarf planet or small solar system body, often called a moon
nautical mile
unit used in measuring distances at sea equal to approximately 2,025 yards or 1,852 meters
navigable waters
waters that are subject to tidal action and those that may be used for interstate or foreign commerce
neap tide
a tide just after the first or third quarters of the Moon when there is least difference between high and low water
negative environmental feedback loop
an environmental process that diminishes the effect of climate forcing
neopelagic
refers to a marine environment in the Great Garbage Patch were open-ocean and coastal species live together

 nepheline
a silica-undersaturated aluminosilicate that occurs in intrusive and volcanic rocks with low silica, and in their associated pegmatites
net zero urban water (NZUW)
approach which meets the needs of a given community with a locally available and sustainable water supply, without detriment to interconnected systems or long-term water supply
nephelometric turbidity unit (NTU)
unit that expresses water turbidity
neucleobase
nitrogen-containing biological compound that forms nucleosides
neucleoside
glycosylamine considered as a nucleotide without a phosphate group
neucleotide
organic molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate
net neutral recharge
volume of water naturally recharging the groundwater supply minus natural depletions to the groundwater supply
neutron
a neutrally-charged subatomic particle in atomic nuclei
new large landscape user
a non-residential facility with water-intensive landscaping of more than 10,000 square feet that has landscaping planted or bodies of water, other than pools,
establised after January 1, 1990, schools, parks, cemetaries, golf courses, common housing areas and recreational facilities are excluded
new large municipal provider
a municipal provider that serves more than 250 acre-feet for non-irrigation purposes during a calendar year
newly turfed area
land planted with warm-season grass that was not planted in the previous calendar year
new sources standards of performance (NSPS)
reflect effluent reductions based on the best available demonstrated control technology
What are the 4 main neucleobases found in DNA and RNA?
newton
force that would give a mass of one kilogram an acceleration of one meter per second per second
nickel
a silver-white hard malleable, ductile, metallic element capable of a high polish and resistant to corrosion used in alloys and as a catalyst
nimbostratus
a type of cloud forming a thick uniform gray layer at low altitude, from which rain or snow often falls, without any lightning or thunder
nepheline
a silica-undersaturated aluminosilicate that occurs in intrusive and volcanic rocks with low silica, and in their associated pegmatites
net zero urban water (NZUW)
approach which meets the needs of a given community with a locally available and sustainable water supply, without detriment to interconnected systems or long-term water supply
nephelometric turbidity unit (NTU)
unit that expresses water turbidity
neucleobase
nitrogen-containing biological compound that forms nucleosides
neucleoside
glycosylamine considered as a nucleotide without a phosphate group
neucleotide
organic molecules composed of a nitrogenous base, a pentose sugar and a phosphate
net neutral recharge
volume of water naturally recharging the groundwater supply minus natural depletions to the groundwater supply
neutron
a neutrally-charged subatomic particle in atomic nuclei
new large landscape user
a non-residential facility with water-intensive landscaping of more than 10,000 square feet that has landscaping planted or bodies of water, other than pools,
establised after January 1, 1990, schools, parks, cemetaries, golf courses, common housing areas and recreational facilities are excluded
new large municipal provider
a municipal provider that serves more than 250 acre-feet for non-irrigation purposes during a calendar year
newly turfed area
land planted with warm-season grass that was not planted in the previous calendar year
new sources standards of performance (NSPS)
reflect effluent reductions based on the best available demonstrated control technology
What are the 4 main neucleobases found in DNA and RNA?
newton
force that would give a mass of one kilogram an acceleration of one meter per second per second
nickel
a silver-white hard malleable, ductile, metallic element capable of a high polish and resistant to corrosion used in alloys and as a catalyst
nimbostratus
a type of cloud forming a thick uniform gray layer at low altitude, from which rain or snow often falls, without any lightning or thunder

 normal fault
a dip-slip fault in which the block above the fault has moved downward relative to the block below
normal flow rights
entitlements to unregulated or natural flow of water in the Salt and Verde Rivers as it existed before construction of SRP reservoirs
normal storage capacity
total volume in acre-feet at normal retention level
Northerly international Boundary (NIB)
border above the Morales Dam 1.1 miles downstream from the California-Baja California land boundary between Los Algodones and Yuma County
Northern Hemisphere
the half of the Earth north of the equator
nucleic acid
a complex organic substance present in living cells, especially DNA or RNA, whose molecules consist of many nucleotides linked in a long chain
nucleoside
a nucleotide with a sugar attached
nucleotide
a compound consisting of a nucleoside linked to a phosphate group, forms the basic structural unit of nucleic acids such as DNA
nuisance flood
shallow flood resulting from higher sea level, wash over roads and into storm drains during high tide
O ↑
normal fault
a dip-slip fault in which the block above the fault has moved downward relative to the block below
normal flow rights
entitlements to unregulated or natural flow of water in the Salt and Verde Rivers as it existed before construction of SRP reservoirs
normal storage capacity
total volume in acre-feet at normal retention level
Northerly international Boundary (NIB)
border above the Morales Dam 1.1 miles downstream from the California-Baja California land boundary between Los Algodones and Yuma County
Northern Hemisphere
the half of the Earth north of the equator
nucleic acid
a complex organic substance present in living cells, especially DNA or RNA, whose molecules consist of many nucleotides linked in a long chain
nucleoside
a nucleotide with a sugar attached
nucleotide
a compound consisting of a nucleoside linked to a phosphate group, forms the basic structural unit of nucleic acids such as DNA
nuisance flood
shallow flood resulting from higher sea level, wash over roads and into storm drains during high tide
O ↑
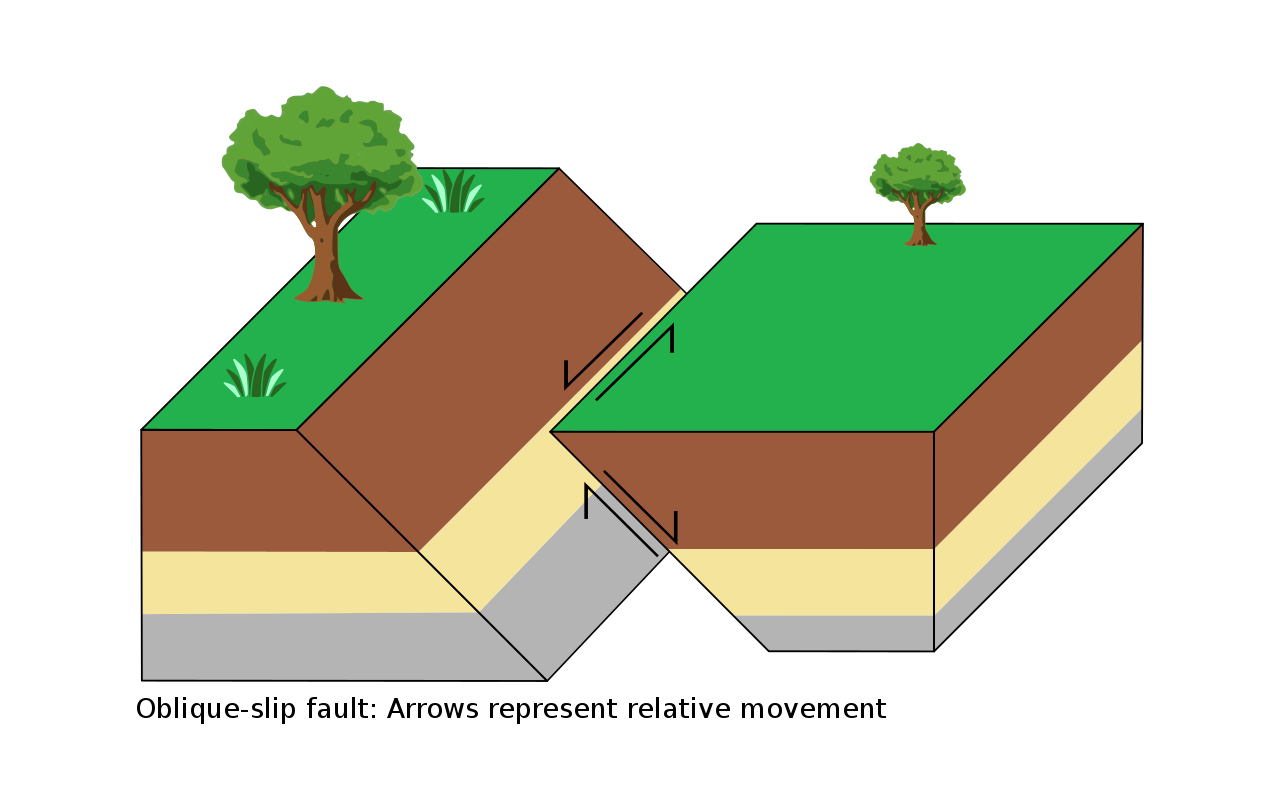

 omphacite
a member of the pyroxene group of silicate minerals, ((Ca, Na)(Mg, Fe2+, Al)Si2O6)
on-farm irrigation efficiency
total water requirements to produce crop divided by the total quantity of water applied to the crop during growing season
ooid
small, spheroidal, coated sedimentary grains, usually composed of calcium carbonate, iron or phosphate-based minerals, usually form on the sea floor in shallow tropical seas
open ditch system
supplied water runs across the upper end of a field
oreodont
an extinct, four-toed, ruminant, artiodactyl mammal of the Merycoidodontidae and Agriochoeridae families living in North America from the Eocene to the early Pliocene and resembling swine
organelle
an organized or specialized structure in a living cell
organic (agriculture)
produced or involving production without the use of chemical fertilizers, pesticides or other artificial substances
organic (biology)
related to living matter
omphacite
a member of the pyroxene group of silicate minerals, ((Ca, Na)(Mg, Fe2+, Al)Si2O6)
on-farm irrigation efficiency
total water requirements to produce crop divided by the total quantity of water applied to the crop during growing season
ooid
small, spheroidal, coated sedimentary grains, usually composed of calcium carbonate, iron or phosphate-based minerals, usually form on the sea floor in shallow tropical seas
open ditch system
supplied water runs across the upper end of a field
oreodont
an extinct, four-toed, ruminant, artiodactyl mammal of the Merycoidodontidae and Agriochoeridae families living in North America from the Eocene to the early Pliocene and resembling swine
organelle
an organized or specialized structure in a living cell
organic (agriculture)
produced or involving production without the use of chemical fertilizers, pesticides or other artificial substances
organic (biology)
related to living matter

 organic compound
a chemical compound in which carbon atoms are are linked to hydrogen, oxygen or nitrogen atoms
organic contaminants
organic compound
a chemical compound in which carbon atoms are are linked to hydrogen, oxygen or nitrogen atoms
organic contaminants

 orthoclase
a white or pink crystal rock-forming mineral rich in feldspar
osmosis
movement of water molecules through a thin membrane
osmotic pressure
pressure that would have to be applied to a pure solvent to prevent it from passing into a given solution by osmosis
outfall
outlet where reclaimed water is discharged into a water body
outflow
all water leaving a water system
outstanding remarkable value (ORV)
a river-related value must be a unique, rare, or exemplary feature that is
significant at a comparative regional or national scale, and can be scenic, recreational, geological, fish-related, wildlife-related, historic, cultural, botanical,
hydrological, paleontological, scientific or other value
overdraft
condition that results when more water is pumped out of an aquifer than is being naturally recharged
overseeded area
an area of land planted with cool-season grass that grows over a dormant warm-season grass
outer core
a fluid layer about 2,260 km (1,400 mi) thick composed of mostly iron and nickel that lies above Earth's solid inner core and below its mantle
oxbow lake
a curved lake formed where the main stream of a river has cut across the narrow end and no longer flows around the loop of the bend
oxidane
the official chemical name for water
oxidation-reduction reaction
a type of chemical reaction that involves a transfer of electrons between two substances
oxidation ditch
a component of the wastewater treatment process that provides long-term aeration, consists of a long channel laid out in an elliptical or circular configuration,
the channel includes mechanical aeration equipment, such as brush rotors, disc aerators, draft tube aerators, or fine bubble diffusers
orthoclase
a white or pink crystal rock-forming mineral rich in feldspar
osmosis
movement of water molecules through a thin membrane
osmotic pressure
pressure that would have to be applied to a pure solvent to prevent it from passing into a given solution by osmosis
outfall
outlet where reclaimed water is discharged into a water body
outflow
all water leaving a water system
outstanding remarkable value (ORV)
a river-related value must be a unique, rare, or exemplary feature that is
significant at a comparative regional or national scale, and can be scenic, recreational, geological, fish-related, wildlife-related, historic, cultural, botanical,
hydrological, paleontological, scientific or other value
overdraft
condition that results when more water is pumped out of an aquifer than is being naturally recharged
overseeded area
an area of land planted with cool-season grass that grows over a dormant warm-season grass
outer core
a fluid layer about 2,260 km (1,400 mi) thick composed of mostly iron and nickel that lies above Earth's solid inner core and below its mantle
oxbow lake
a curved lake formed where the main stream of a river has cut across the narrow end and no longer flows around the loop of the bend
oxidane
the official chemical name for water
oxidation-reduction reaction
a type of chemical reaction that involves a transfer of electrons between two substances
oxidation ditch
a component of the wastewater treatment process that provides long-term aeration, consists of a long channel laid out in an elliptical or circular configuration,
the channel includes mechanical aeration equipment, such as brush rotors, disc aerators, draft tube aerators, or fine bubble diffusers



 peneplain
a level land surface produced by prolonged erosion
per capita use
average amount of water used per person during a certain time
perchlorate
the anion created when perchloric acid and its salts dissociate in water
percolation
process of a liquid slowly passing through a filter or the ground
perennial
present all seasons of the year
perennial stream
refers to a stream which flows throughout the year through at least parts of its stream bed during years of normal rainfall
perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS)
a chemical used in stain-resistant fabrics, fire-fighting foams, food packaging and as a surfactant in industrial processes
perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA)
a manufactured perfluorochemical and a byproduct in producing fluoropolymers
perfluorotributylamine
organofluorine compound and greenhouse gas in which all the hydrogens have been replaced by fluorine atoms
peneplain
a level land surface produced by prolonged erosion
per capita use
average amount of water used per person during a certain time
perchlorate
the anion created when perchloric acid and its salts dissociate in water
percolation
process of a liquid slowly passing through a filter or the ground
perennial
present all seasons of the year
perennial stream
refers to a stream which flows throughout the year through at least parts of its stream bed during years of normal rainfall
perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS)
a chemical used in stain-resistant fabrics, fire-fighting foams, food packaging and as a surfactant in industrial processes
perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA)
a manufactured perfluorochemical and a byproduct in producing fluoropolymers
perfluorotributylamine
organofluorine compound and greenhouse gas in which all the hydrogens have been replaced by fluorine atoms
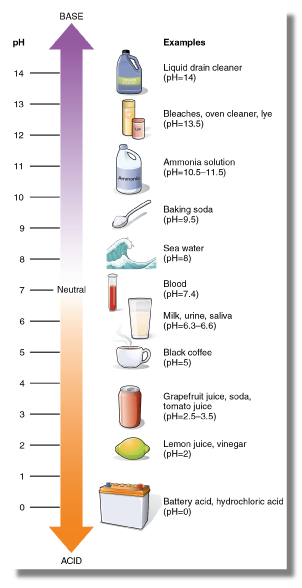

 physiology
the branch of biology that deals with the normal functions of living organisms and their parts
phytoplankton
plankton consisting of microscopic plants
piedmont
a gentle slope leading from the base of mountains to a region of flat land
piedmont glacier
a fan or lobe-shaped glacier, located at the front of a mountain range
piezometer
device which measures the pressure of groundwater at a specific point
pillow lava
lava with a pillow-shaped structure attributed to the extrusion of lava underwater
pinnacle
a high, pointed piece of rock
plagioclase
a typically white form of feldspar consisting of aluminosilicates of sodium or calcium, common in igneous rocks
planetary science
the science of the similarities and differences of planetary bodies
plankton
the small and microscopic organisms drifting or floating in the sea or fresh water, consisting of diatoms, protozoans, small crustaceans, and the eggs and larval stages of larger animals
physiology
the branch of biology that deals with the normal functions of living organisms and their parts
phytoplankton
plankton consisting of microscopic plants
piedmont
a gentle slope leading from the base of mountains to a region of flat land
piedmont glacier
a fan or lobe-shaped glacier, located at the front of a mountain range
piezometer
device which measures the pressure of groundwater at a specific point
pillow lava
lava with a pillow-shaped structure attributed to the extrusion of lava underwater
pinnacle
a high, pointed piece of rock
plagioclase
a typically white form of feldspar consisting of aluminosilicates of sodium or calcium, common in igneous rocks
planetary science
the science of the similarities and differences of planetary bodies
plankton
the small and microscopic organisms drifting or floating in the sea or fresh water, consisting of diatoms, protozoans, small crustaceans, and the eggs and larval stages of larger animals


 precipitable water
a measure of the total amount of water vapor contained in a small vertical column extending from the surface to the top of the atmosphere
precipitate
the process of being deposited as a solid out of a solution
precipitation
any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravity, includes drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, graupel and hail
preliminary treatment
removal of suspended and floating particles
pretreatment standards for existing sources (PSES)
national, uniform, technology-based standards that apply to indirect dischargers
pretreatment standards for new sources (PSNS)
national, uniform, technology-based standards that apply to new indirect dischargers
primary treatment
first stage in wastewater treatment where some solids and organic material are removed by screening and sedimentation
prime meridian
an arbitrary line of longitude in a geographic coordinate system at which longitude is defined to be 0o
prior appropriation doctrine
precipitable water
a measure of the total amount of water vapor contained in a small vertical column extending from the surface to the top of the atmosphere
precipitate
the process of being deposited as a solid out of a solution
precipitation
any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravity, includes drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, graupel and hail
preliminary treatment
removal of suspended and floating particles
pretreatment standards for existing sources (PSES)
national, uniform, technology-based standards that apply to indirect dischargers
pretreatment standards for new sources (PSNS)
national, uniform, technology-based standards that apply to new indirect dischargers
primary treatment
first stage in wastewater treatment where some solids and organic material are removed by screening and sedimentation
prime meridian
an arbitrary line of longitude in a geographic coordinate system at which longitude is defined to be 0o
prior appropriation doctrine


 rain shadow
dry area on the leeward side of a mountain, away from the wind
rainshadow desert
a patch of land that has become a desert because mountain ranges block much of the rainfall necessary for plant growth
rainwater harvesting
collecting rain from roofs, patios and other surfaces
range
a series of continuous townships aligned north and south and numbered east to west from a prime meridian
rarefaction
relating to the spreading of gas particles
rating height
a data curve that shows the relationship between gage height data and stream discharge height
ravine
a deep, narrow gorge with steep sides
reach
length of a stream or river
recent stream alluvium
unconsolidated clay, sand, silt or gravel recently deposited by a stream
recessional moraine
series of ridges that run across a valley behind a terminal moraine
recharge
replenishing an aquifer by surface infiltration or by other natural or induced means
reciprocating internal combustion engine (RICE)
engine that uses gas expnasion and increased pressure from fuel combustion to move pistons
rain shadow
dry area on the leeward side of a mountain, away from the wind
rainshadow desert
a patch of land that has become a desert because mountain ranges block much of the rainfall necessary for plant growth
rainwater harvesting
collecting rain from roofs, patios and other surfaces
range
a series of continuous townships aligned north and south and numbered east to west from a prime meridian
rarefaction
relating to the spreading of gas particles
rating height
a data curve that shows the relationship between gage height data and stream discharge height
ravine
a deep, narrow gorge with steep sides
reach
length of a stream or river
recent stream alluvium
unconsolidated clay, sand, silt or gravel recently deposited by a stream
recessional moraine
series of ridges that run across a valley behind a terminal moraine
recharge
replenishing an aquifer by surface infiltration or by other natural or induced means
reciprocating internal combustion engine (RICE)
engine that uses gas expnasion and increased pressure from fuel combustion to move pistons


 respiration
a process in living organisms involving the production of energy, typically with the intake of oxygen and the release of carbon dioxide from the oxidation of complex organic substances
return activated sludge (RAS)
settled activated sludge that is collected in the secondary clarifier or the membrane basin and returned to the aeration basin to mix with incoming raw or primary settled wastewater
return flow
water that reaches a groundwater source after release from its use point, becoming available for further use
reverse fault
the hanging wall moves up relative to the footwall
reverse osmosis (RO)
when a solvent passes through a porous membrane in the direction opposite to that for natural osmosis when subjected to a hydrostatic pressure greater than the osmotic pressure
revolution
refers to Earth's orbit around the Sun of approximately 365 days, 6 hours, 9 minutes
rhyolite
an extrusive igneous rock with a very high silica content, usually pink or gray in color with grains so small that they are difficult to observe without a hand lens,
made up of quartz, plagioclase, and sanidine, with minor amounts of hornblende and biotite
ribbon reef
long, narrow, winding reef, usually associated with an atoll lagoon
ribonucleic acid (RNA)
converting genetic information from genes into the amino acid sequences of proteins
ridge (geology)
a long narrow hilltop, mountain range, or watershed
ridge (meteorology)
an elongated area of relatively high atmospheric pressure
respiration
a process in living organisms involving the production of energy, typically with the intake of oxygen and the release of carbon dioxide from the oxidation of complex organic substances
return activated sludge (RAS)
settled activated sludge that is collected in the secondary clarifier or the membrane basin and returned to the aeration basin to mix with incoming raw or primary settled wastewater
return flow
water that reaches a groundwater source after release from its use point, becoming available for further use
reverse fault
the hanging wall moves up relative to the footwall
reverse osmosis (RO)
when a solvent passes through a porous membrane in the direction opposite to that for natural osmosis when subjected to a hydrostatic pressure greater than the osmotic pressure
revolution
refers to Earth's orbit around the Sun of approximately 365 days, 6 hours, 9 minutes
rhyolite
an extrusive igneous rock with a very high silica content, usually pink or gray in color with grains so small that they are difficult to observe without a hand lens,
made up of quartz, plagioclase, and sanidine, with minor amounts of hornblende and biotite
ribbon reef
long, narrow, winding reef, usually associated with an atoll lagoon
ribonucleic acid (RNA)
converting genetic information from genes into the amino acid sequences of proteins
ridge (geology)
a long narrow hilltop, mountain range, or watershed
ridge (meteorology)
an elongated area of relatively high atmospheric pressure

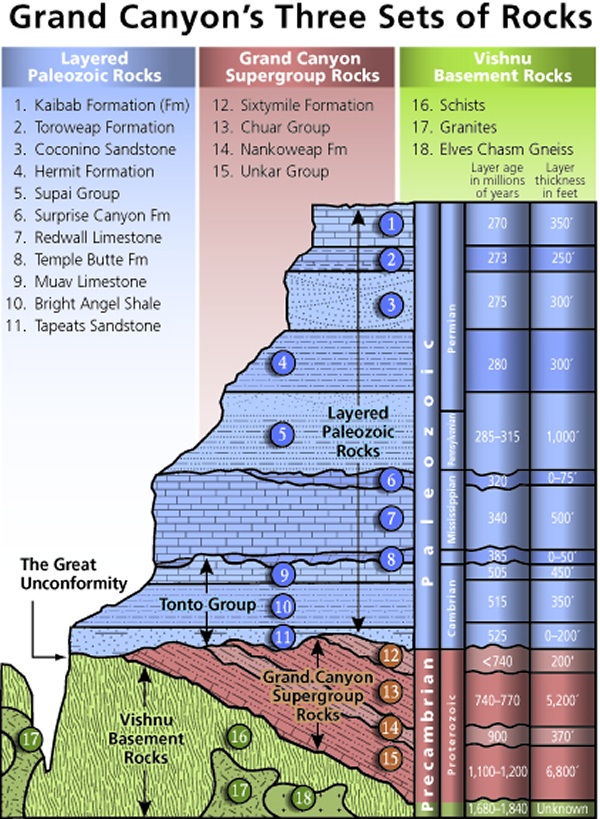
 rock
any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals
rock cycle
explains how rock transforms sedimentary, metamorphic and igneous types due to pressure, temperature and weathering
rock glacier
a glacier-like landform that consists of a valley-filling accumulation of angular rock blocks, has little or no visible surface ice
rock unit
aggregations of lithologic constituents with particular relationships
rogen moraine
forms a series of ribs at right angles to the direction of the glacier flow
rogue wave
wave greater than twice the size of surrounding waves
Rossby wave
also known as planetary waves, occur naturally in rotating fluids, in Earth's ocean and atmosphere they form as a result of our planet's rotation
runaway greenhouse effect
occurs when a planet's atmosphere contains greenhouse gases that block heat escaping from the planet, preventing the planet from cooling and from having liquid water on its surface
runoff
water drainage from the surface of a land area
S ↑
safe yield
long-term balance between the amount of groundwater withdrawn annually and the annual amount of natural and artificial recharge in an active management area
Saffir-Simpson scale
classifies hurricanes and tropical cyclones, that exceed intensities of tropical depressions and tropical storms, into five categories distinguished by sustained wind intensities
sagebrush
a shrubby aromatic North American plant of the daisy family
saline
containing salt
salinity
the degree to which something is salty
rock
any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals
rock cycle
explains how rock transforms sedimentary, metamorphic and igneous types due to pressure, temperature and weathering
rock glacier
a glacier-like landform that consists of a valley-filling accumulation of angular rock blocks, has little or no visible surface ice
rock unit
aggregations of lithologic constituents with particular relationships
rogen moraine
forms a series of ribs at right angles to the direction of the glacier flow
rogue wave
wave greater than twice the size of surrounding waves
Rossby wave
also known as planetary waves, occur naturally in rotating fluids, in Earth's ocean and atmosphere they form as a result of our planet's rotation
runaway greenhouse effect
occurs when a planet's atmosphere contains greenhouse gases that block heat escaping from the planet, preventing the planet from cooling and from having liquid water on its surface
runoff
water drainage from the surface of a land area
S ↑
safe yield
long-term balance between the amount of groundwater withdrawn annually and the annual amount of natural and artificial recharge in an active management area
Saffir-Simpson scale
classifies hurricanes and tropical cyclones, that exceed intensities of tropical depressions and tropical storms, into five categories distinguished by sustained wind intensities
sagebrush
a shrubby aromatic North American plant of the daisy family
saline
containing salt
salinity
the degree to which something is salty


 sandstone
sedimentary rock composed of sand-size grains of mineral, rock, or organic material
sanitary sewer
a pipe that carries wastewater from residences, commercial buildings, industrial plants or institutions
Sargassum
brown algae with leafy segments, air bladders or spore-bearing structures
sauropod
a very large plant-eating quadruped dinosaur with a long neck and tail, small head and massive limbs
sea
a water body smaller than an ocean but larger than a lake
sea breeze
wind blowing from a large body of water toward land due to air pressure differences created by different heat capacities of water and dry land
seamount
a large ocean mountain that does not rise above the sea surface
scablands
flat elevated land scarred by channels of glacial or fluvioglacial origin and with poor soil and little vegetation, especially in the Columbia Plateau of Washington State
schist
coarse-grained metamorphic rock which consists of layers of different minerals and can be split into thin irregular plates
science
the intellectual and practical activity encompassing the systematic study of the structure and behaviour of the physical and natural world through observation and experiment
scientific method
an empirical method of acquiring knowledge involving careful observation, applying rigorous skepticism about what is observed, formulating hypotheses via induction, based on such observations, experimental and measurement-based testing of deductions drawn from the hypotheses, and refinement or elimination of the hypotheses based on the experimental findings
sandstone
sedimentary rock composed of sand-size grains of mineral, rock, or organic material
sanitary sewer
a pipe that carries wastewater from residences, commercial buildings, industrial plants or institutions
Sargassum
brown algae with leafy segments, air bladders or spore-bearing structures
sauropod
a very large plant-eating quadruped dinosaur with a long neck and tail, small head and massive limbs
sea
a water body smaller than an ocean but larger than a lake
sea breeze
wind blowing from a large body of water toward land due to air pressure differences created by different heat capacities of water and dry land
seamount
a large ocean mountain that does not rise above the sea surface
scablands
flat elevated land scarred by channels of glacial or fluvioglacial origin and with poor soil and little vegetation, especially in the Columbia Plateau of Washington State
schist
coarse-grained metamorphic rock which consists of layers of different minerals and can be split into thin irregular plates
science
the intellectual and practical activity encompassing the systematic study of the structure and behaviour of the physical and natural world through observation and experiment
scientific method
an empirical method of acquiring knowledge involving careful observation, applying rigorous skepticism about what is observed, formulating hypotheses via induction, based on such observations, experimental and measurement-based testing of deductions drawn from the hypotheses, and refinement or elimination of the hypotheses based on the experimental findings

 self-propelled traveler system
a large single water gun mounted on a trailer or cart that projects water through a single nozzle up to 200 feet
self-supplied water
water obtained from a private well
septic tank
a tank used to hold domestic water wastes
serpentinite
a metamorphic rock that is mostly composed of ultramific rocks that have undergone hydrous alteration
service area right
the right of a city, town, private water company or irrigation district within an active management area to withdraw and deliver groundwater to customers
service connection
the physical connection between a municipal water system and its customer
settling pond
an open lagoon that stores waste water and allows contaminants to sink
sewage
untreated wastes from toilets, baths, sinks, laundries and other plumbing fixtures in places of human habitation, employment or recreation
sewage treatment plant
a facility that eliminates many pollutants from wastewater
sewer
an underground pipe system that transports wastewater to treatment facilities
What are the 4 forests in the Four Forest Restoration Initiative?
shadescale
a small shrub with woody, thorny branches and leaves with a whitish, scale-like coating
shale
soft, finely stratified sedimentary rock that formed from consolidated mud or clay and can be split easily into fragile slabs
shield
a large area of exposed Precambrian crystalline igneous and high-grade metamorphic rocks that form tectonically stable areas
self-propelled traveler system
a large single water gun mounted on a trailer or cart that projects water through a single nozzle up to 200 feet
self-supplied water
water obtained from a private well
septic tank
a tank used to hold domestic water wastes
serpentinite
a metamorphic rock that is mostly composed of ultramific rocks that have undergone hydrous alteration
service area right
the right of a city, town, private water company or irrigation district within an active management area to withdraw and deliver groundwater to customers
service connection
the physical connection between a municipal water system and its customer
settling pond
an open lagoon that stores waste water and allows contaminants to sink
sewage
untreated wastes from toilets, baths, sinks, laundries and other plumbing fixtures in places of human habitation, employment or recreation
sewage treatment plant
a facility that eliminates many pollutants from wastewater
sewer
an underground pipe system that transports wastewater to treatment facilities
What are the 4 forests in the Four Forest Restoration Initiative?
shadescale
a small shrub with woody, thorny branches and leaves with a whitish, scale-like coating
shale
soft, finely stratified sedimentary rock that formed from consolidated mud or clay and can be split easily into fragile slabs
shield
a large area of exposed Precambrian crystalline igneous and high-grade metamorphic rocks that form tectonically stable areas
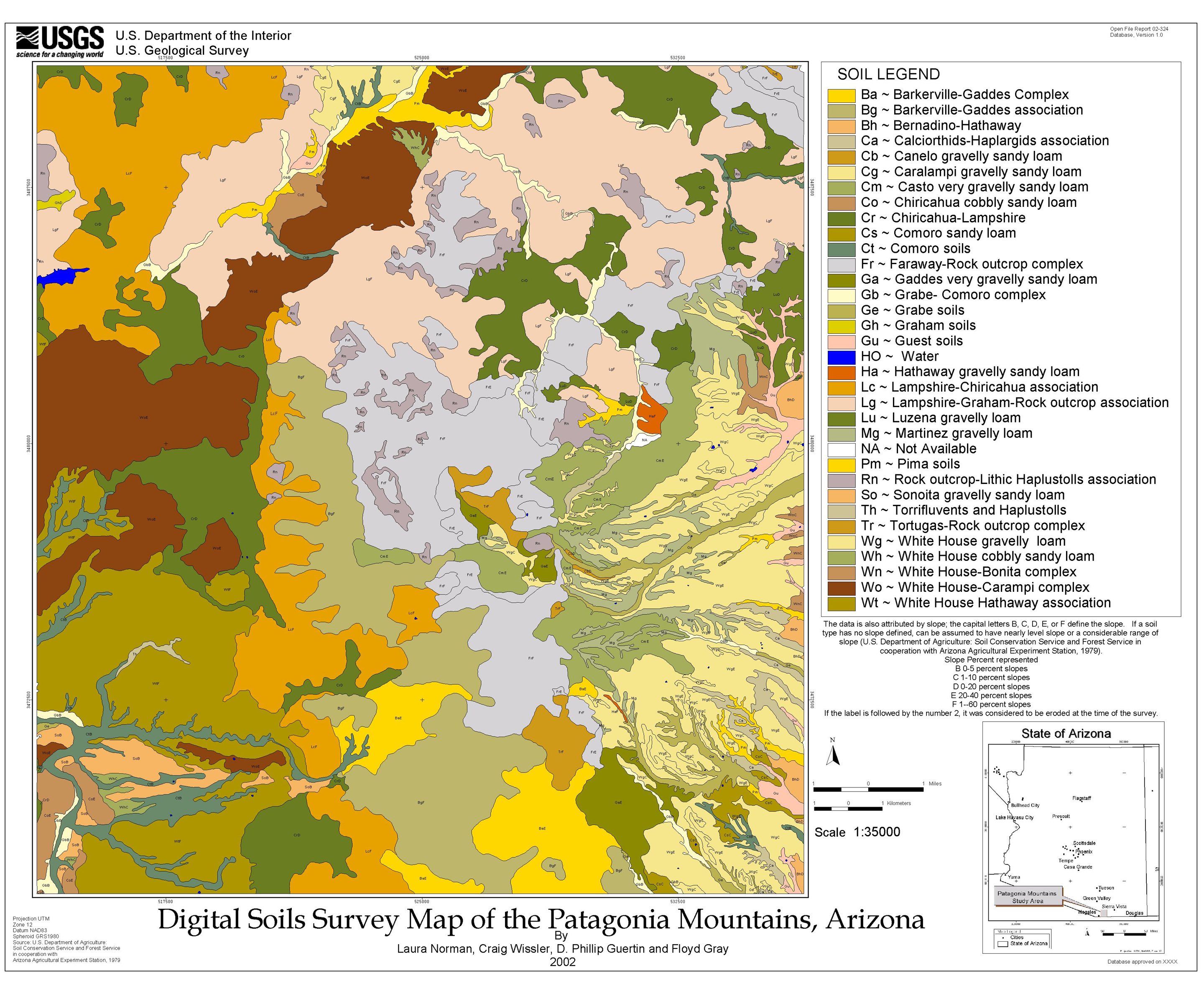
 slug test
aquifer test where water is quickly added or removed from a groundwater well and the change in hydraulic head is monitored through time
slump
created when a mass of loosely consolidated materials or a rock layer moves a short distance down a slope
small community water system
a community water system that annually serves 1,850 acre-feet or less of water to customers
small municipal provider
a municipal provider within an active management area that serves 250 acre-feet or less of water for non-irrigation purposes
smectite
hydrous aluminum silicates containing iron and magnesium as well as either sodium or calcium
snow
ice crystal precipitation
snowpack
a compressed and hardened snow mass
snow water equivalent (SWE)
amount of water contained in snowpack that would theoretically appear if the snow were melted
soda
sodium carbonate, especially as a natural mineral or as an industrial chemical
sodium
a silver-white, soft, waxy, ductile, chemically-active element that occurs abundantly in nature
sodium bisulfate
an acid salt formed by partial neutralization of sulfuric acid by an equivalent of sodium base, (NaHSO4)
slug test
aquifer test where water is quickly added or removed from a groundwater well and the change in hydraulic head is monitored through time
slump
created when a mass of loosely consolidated materials or a rock layer moves a short distance down a slope
small community water system
a community water system that annually serves 1,850 acre-feet or less of water to customers
small municipal provider
a municipal provider within an active management area that serves 250 acre-feet or less of water for non-irrigation purposes
smectite
hydrous aluminum silicates containing iron and magnesium as well as either sodium or calcium
snow
ice crystal precipitation
snowpack
a compressed and hardened snow mass
snow water equivalent (SWE)
amount of water contained in snowpack that would theoretically appear if the snow were melted
soda
sodium carbonate, especially as a natural mineral or as an industrial chemical
sodium
a silver-white, soft, waxy, ductile, chemically-active element that occurs abundantly in nature
sodium bisulfate
an acid salt formed by partial neutralization of sulfuric acid by an equivalent of sodium base, (NaHSO4)
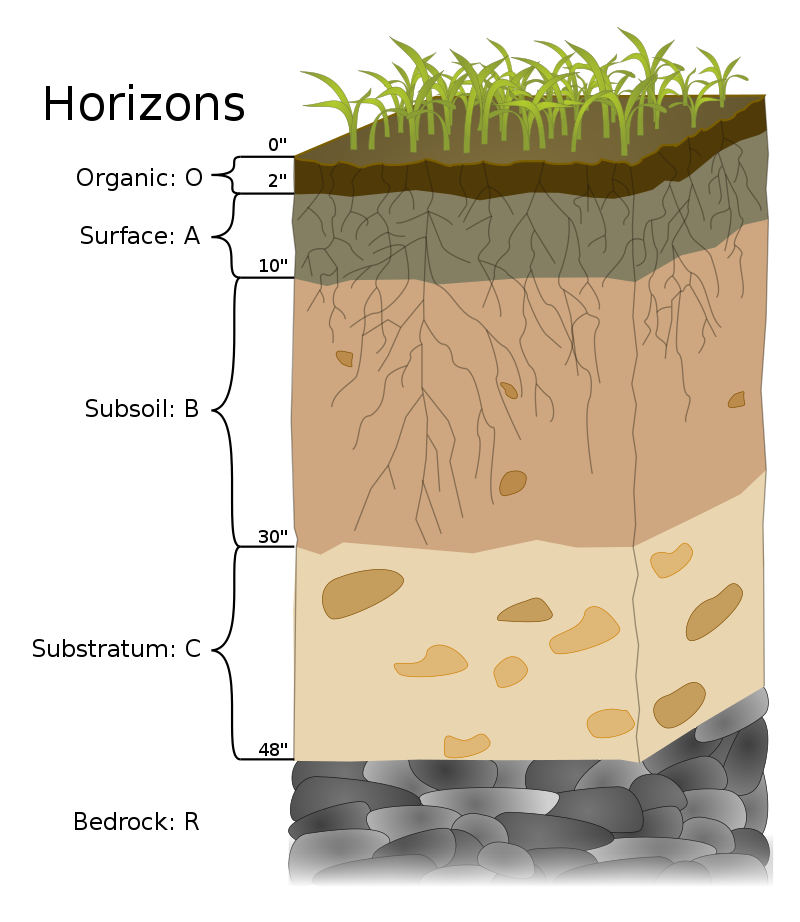




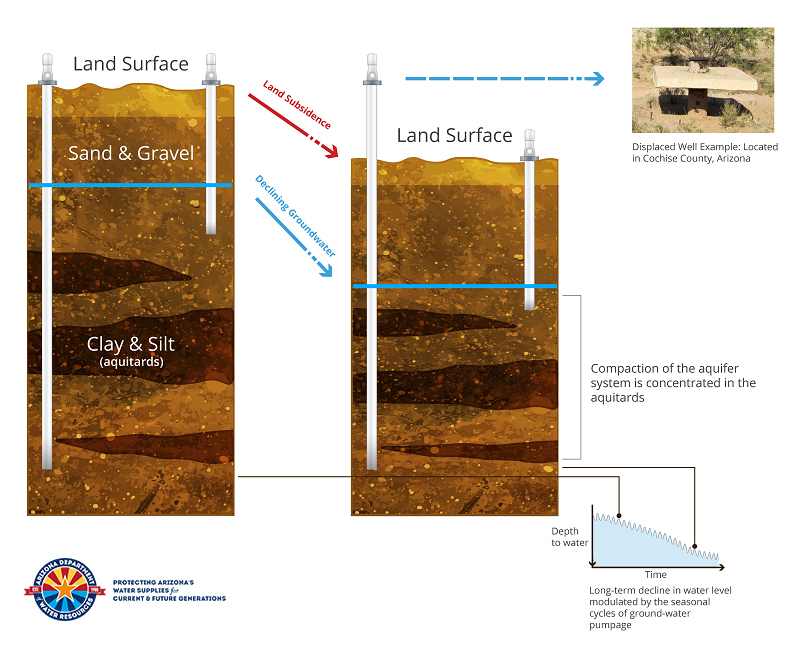
 sublimation
transition of a substance directly from the solid to the gas phase, without passing through the intermediate liquid phase
submarine canyon
a steep-sided valley cut into the seabed of the continental slope
submarine river
a river-like current on the seabed
sub-regional
non-metropolitan wastewater reclamation facilities operated by Pima County, including Arivaca Junction, Avra Valley, Corona de Tucson, Green Valley,
Mount Lemmon, and Pima County Fairgrounds
subsidence
the downward movement or sinking of Earth's surface caused by removal of underlying support
subsoil
the soil lying immediately under the surface soil
substratum
an underlying layer of rock or soil beneath the ground
subtropical desert
found along the Tropic of Cancer between 15oN and 30oN of the equator or along the Tropic of Capricorn between 15oN and 30oS of the equator
sulfate
a salt of sulfuric acid, containing the anion SO42-
sulfide
mineral in which metals are bonded to sulfur
sublimation
transition of a substance directly from the solid to the gas phase, without passing through the intermediate liquid phase
submarine canyon
a steep-sided valley cut into the seabed of the continental slope
submarine river
a river-like current on the seabed
sub-regional
non-metropolitan wastewater reclamation facilities operated by Pima County, including Arivaca Junction, Avra Valley, Corona de Tucson, Green Valley,
Mount Lemmon, and Pima County Fairgrounds
subsidence
the downward movement or sinking of Earth's surface caused by removal of underlying support
subsoil
the soil lying immediately under the surface soil
substratum
an underlying layer of rock or soil beneath the ground
subtropical desert
found along the Tropic of Cancer between 15oN and 30oN of the equator or along the Tropic of Capricorn between 15oN and 30oS of the equator
sulfate
a salt of sulfuric acid, containing the anion SO42-
sulfide
mineral in which metals are bonded to sulfur


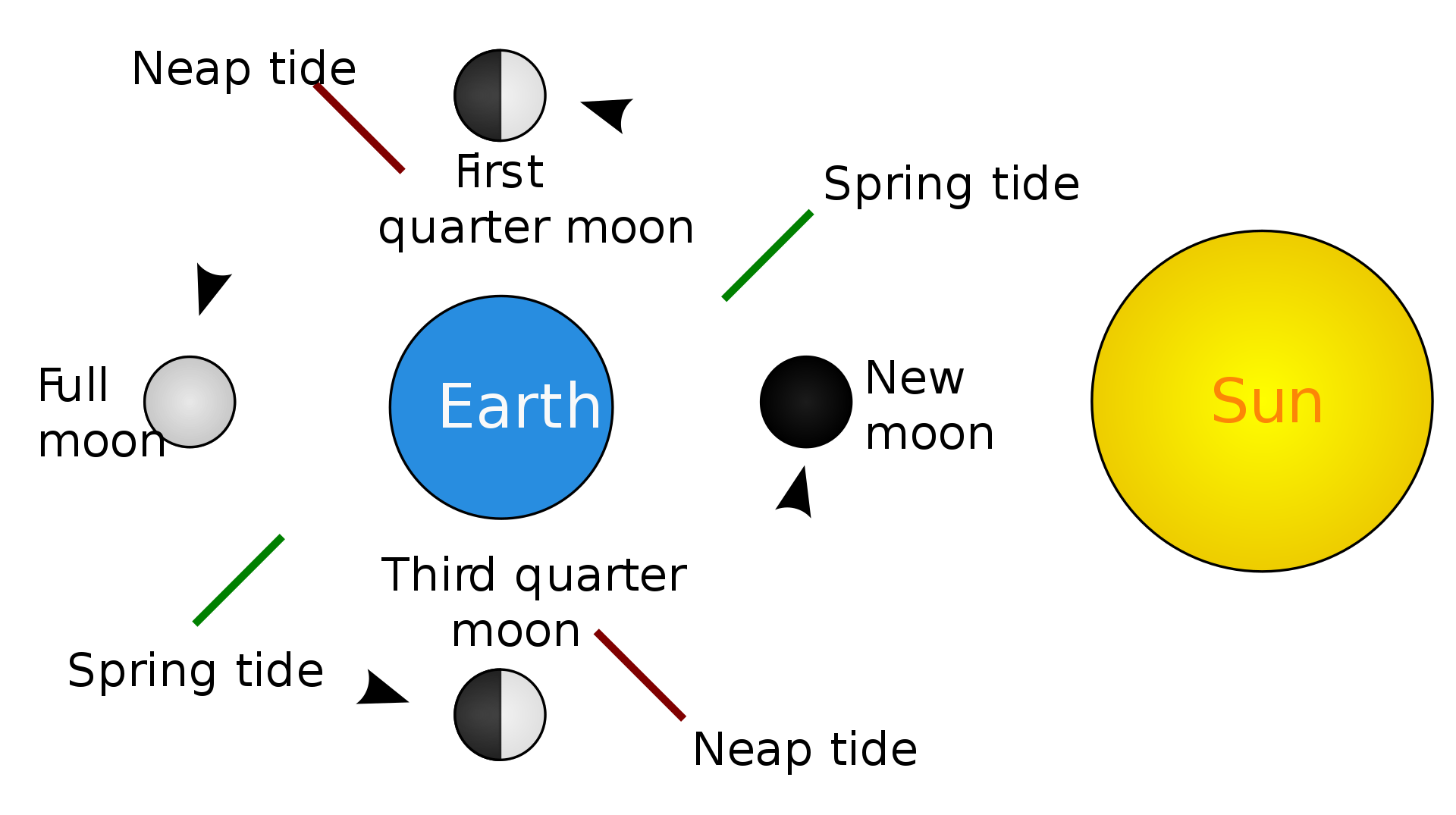
 topography
detailed description or representation on a map of the natural and artificial features of an area
tornado
a large storm that forms over land as a tall, rotating column of air extending from a thunderstorm base to the ground
total dissolved solids (TDS)
describe the inorganic salts and small amounts of organic matter present in solution in water
total Kjedahl nitrogen
a method for determining the amount of nitrogen contained in organic substances plus the nitrogen contained in the inorganic compounds ammonia and ammonium
total maximum daily load (TMDL)
a regulatory term in the U.S. Clean Water Act, describing a plan for restoring impaired waters that identifies the maximum amount of a pollutant that a body of water can receive while still meeting water quality standards
total suspended solids (TSS)
refers to waterborne particles larger than 2 microns in size
tourmaline
crystalline boron silicate mineral compounded with elements such as aluminium, iron, magnesium, sodium, lithium, or potassium
township
a survey unit that represents a piece of land bounded on the east and west by meridians approximately 6 miles apart
trachyte
an igneous volcanic rock with an aphanitic to porphyritic texture
traditionally navigable water (TNW)
those waters that are subject to the ebb and flow of the tide and/or are presently used, or have been used in the past, or may be susceptible for use to transport interstate or foreign commerce
transform fault
occurs when two tectonic plates move past each other
transgression
landward migration of a shoreline, flooding of previously dry land due to sea level rise or subduction
transient flow
a flow field in which the flow velocity at any given point changes with time
transient non-community water system (TNCWS)
a public water system that provides water in a place such as a gas station or campground where people do not remain for long periods of time
translucent
allowing some light to pass through
transmissibility
capacity of rock to transport water under pressure
transmissivity
rate at which water is transmitted through whole thickness and unit width of an aquifer under a unit hydraulic gradient
transpiration
exhalation of water vapor through the stomata of a plant or leaf
transverse valley
valley which cuts at right angles across a ridge or, in mountainous terrain a valley that generally runs at right angles to the line of the main mountain chain or crest
topography
detailed description or representation on a map of the natural and artificial features of an area
tornado
a large storm that forms over land as a tall, rotating column of air extending from a thunderstorm base to the ground
total dissolved solids (TDS)
describe the inorganic salts and small amounts of organic matter present in solution in water
total Kjedahl nitrogen
a method for determining the amount of nitrogen contained in organic substances plus the nitrogen contained in the inorganic compounds ammonia and ammonium
total maximum daily load (TMDL)
a regulatory term in the U.S. Clean Water Act, describing a plan for restoring impaired waters that identifies the maximum amount of a pollutant that a body of water can receive while still meeting water quality standards
total suspended solids (TSS)
refers to waterborne particles larger than 2 microns in size
tourmaline
crystalline boron silicate mineral compounded with elements such as aluminium, iron, magnesium, sodium, lithium, or potassium
township
a survey unit that represents a piece of land bounded on the east and west by meridians approximately 6 miles apart
trachyte
an igneous volcanic rock with an aphanitic to porphyritic texture
traditionally navigable water (TNW)
those waters that are subject to the ebb and flow of the tide and/or are presently used, or have been used in the past, or may be susceptible for use to transport interstate or foreign commerce
transform fault
occurs when two tectonic plates move past each other
transgression
landward migration of a shoreline, flooding of previously dry land due to sea level rise or subduction
transient flow
a flow field in which the flow velocity at any given point changes with time
transient non-community water system (TNCWS)
a public water system that provides water in a place such as a gas station or campground where people do not remain for long periods of time
translucent
allowing some light to pass through
transmissibility
capacity of rock to transport water under pressure
transmissivity
rate at which water is transmitted through whole thickness and unit width of an aquifer under a unit hydraulic gradient
transpiration
exhalation of water vapor through the stomata of a plant or leaf
transverse valley
valley which cuts at right angles across a ridge or, in mountainous terrain a valley that generally runs at right angles to the line of the main mountain chain or crest

 travertine
a white, tan, cream or rust-colored fibrous or concentric limestone mineral deposited by mineral hot springs
treatment
a process that changes the quality of water by physical, chemical, or biological means
trench
long, narrow depressions on the seafloor that form at the boundary of tectonic plates where one plate is pushed beneath another
Triassic
the earliest period of the Mesozoic era, spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.9 million years ago, to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.3 million years ago
tributary
a stream which does not reach a static body of water such as a lake or ocean, but joins another river
trichloroethylene (TCE)
a colorless liquid with a chloroform-like odor
trichlorofluoromethane
a colorless, sweetish-smelling liquid that boils around room temperature becoming an ozone-depleting greenhouse gas
trifluoromethane
a colorless nonflammable greenhouse gas
trihalomethane (THM)
derivatives of methane, such as chloroform, that have three halogen atoms per molecule and can be formed during the chlorination of drinking water
travertine
a white, tan, cream or rust-colored fibrous or concentric limestone mineral deposited by mineral hot springs
treatment
a process that changes the quality of water by physical, chemical, or biological means
trench
long, narrow depressions on the seafloor that form at the boundary of tectonic plates where one plate is pushed beneath another
Triassic
the earliest period of the Mesozoic era, spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.9 million years ago, to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.3 million years ago
tributary
a stream which does not reach a static body of water such as a lake or ocean, but joins another river
trichloroethylene (TCE)
a colorless liquid with a chloroform-like odor
trichlorofluoromethane
a colorless, sweetish-smelling liquid that boils around room temperature becoming an ozone-depleting greenhouse gas
trifluoromethane
a colorless nonflammable greenhouse gas
trihalomethane (THM)
derivatives of methane, such as chloroform, that have three halogen atoms per molecule and can be formed during the chlorination of drinking water


 urban heat island (UHI)
an urban area or metropolitan area that is significantly warmer than its surrounding rural areas due to human activities
use value of water
agricultural production, household and industrial uses, recreational enjoyment of reservoirs, streams, lakes, springs, and ecosystems support
V ↑
vadose
relating to underground water above the water table
valley glacier
a glacier that flows for all or most of its length within the walls of a mountain valley, also called an alpine glacier or a mountain glacier
vapor
substance in a gaseous state
veiki moraine
forms irregular land surfaces of ponds and plateaus
verdure
lush green vegetation
urban heat island (UHI)
an urban area or metropolitan area that is significantly warmer than its surrounding rural areas due to human activities
use value of water
agricultural production, household and industrial uses, recreational enjoyment of reservoirs, streams, lakes, springs, and ecosystems support
V ↑
vadose
relating to underground water above the water table
valley glacier
a glacier that flows for all or most of its length within the walls of a mountain valley, also called an alpine glacier or a mountain glacier
vapor
substance in a gaseous state
veiki moraine
forms irregular land surfaces of ponds and plateaus
verdure
lush green vegetation

 vermiculite
a hydrous phyllosilicate mineral that expands when heated
vertebrate
an animal with a backbone
vesicular
refers to rock pitted with many cavities or small holes where gas was trapped during cooling
virus
an infectious microbe consisting of a DNA or RNA segment surrounded by a protein coat, must infect cells to make copies of itself
viscous
refers to the measure of resistance of a fluid to deformation under stress
viticulture
cultivation and harvesting of grapes
vlei
a marshy depression in which water collects in the wet season
volatile
a substance that easily evaporates at room temperatures
volatile organic compounds (VOC)
organic chemicals that evaporate at room temperature
What is the study of weather?
volcanic bomb
a mass of molten rock larger than 64 millimeters in diameter, formed when a volcano ejects viscous fragments of lava during an eruption
volcanic island
an island created from volcanic eruptions
volcanism
relating to volcanic activity
volcano
a conical mountain or hill having a crater or vent through which lava, rock fragments, hot vapor and gas erupted from Earth's crust
W ↑
What metal is liquid at room temperature?
wadi
the bed or valley of a stream in regions of southwestern Asia and northern Africa that is usually dry except during the rainy season and that often forms an oasis
Walther's Law
sedimentary environments that were side-by-side will end up overlapping each other over time due to transgressions and regressions
waste activated sludge (WAS)
the excess quantity of microorganisms that must be removed from a process to keep the biological system in balance
waste doctrine
takes effect when a water user could utilize water more efficiently but fails to do so, causing the user to forfeit part of that water
What are Earth`s four geologic eons?
wastewater
water discharged after an industrial or municipal use, excluding effluent
wastewater treatment return flow
water returned to a water body from a wastewater treatment plant
water
a transparent, tasteless, odorless, nearly colorless inorganic compound with the chemical formula H2O, the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms
vermiculite
a hydrous phyllosilicate mineral that expands when heated
vertebrate
an animal with a backbone
vesicular
refers to rock pitted with many cavities or small holes where gas was trapped during cooling
virus
an infectious microbe consisting of a DNA or RNA segment surrounded by a protein coat, must infect cells to make copies of itself
viscous
refers to the measure of resistance of a fluid to deformation under stress
viticulture
cultivation and harvesting of grapes
vlei
a marshy depression in which water collects in the wet season
volatile
a substance that easily evaporates at room temperatures
volatile organic compounds (VOC)
organic chemicals that evaporate at room temperature
What is the study of weather?
volcanic bomb
a mass of molten rock larger than 64 millimeters in diameter, formed when a volcano ejects viscous fragments of lava during an eruption
volcanic island
an island created from volcanic eruptions
volcanism
relating to volcanic activity
volcano
a conical mountain or hill having a crater or vent through which lava, rock fragments, hot vapor and gas erupted from Earth's crust
W ↑
What metal is liquid at room temperature?
wadi
the bed or valley of a stream in regions of southwestern Asia and northern Africa that is usually dry except during the rainy season and that often forms an oasis
Walther's Law
sedimentary environments that were side-by-side will end up overlapping each other over time due to transgressions and regressions
waste activated sludge (WAS)
the excess quantity of microorganisms that must be removed from a process to keep the biological system in balance
waste doctrine
takes effect when a water user could utilize water more efficiently but fails to do so, causing the user to forfeit part of that water
What are Earth`s four geologic eons?
wastewater
water discharged after an industrial or municipal use, excluding effluent
wastewater treatment return flow
water returned to a water body from a wastewater treatment plant
water
a transparent, tasteless, odorless, nearly colorless inorganic compound with the chemical formula H2O, the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms
 water duty
amount of water that is reasonable to apply to irrigated land to produce crops based on location, soil, consumptive use, evaporation and seepage
water equity
occurs when all communities have access to safe, clean, affordable drinking water and wastewater services,
participate in community water-related decision-making processes related to water and share in the economic, social and environmental benefits of water systems
water harvesting
process of intercepting stormwater from a surface, such as a roof, parking area, or land surface, and putting it to beneficial use
water-intensive landscaped area
any area of land that is not planted with ADWR's Low Water Use/Drought Tolerant Plant list
waterpocket
refers to the potholes that dot sandstone and fill with rainwater
water quality
the chemical, physical and biological characteristics of water based on usage standards
water reclamation
also known as water recycling or water reuse, reclaims water from a variety of sources then treats and reuses it for agriculture and irrigation,
potable water supplies, groundwater replenishment, industrial processes and environmental restoration
water recycling
also known as water reclamation or water reuse
The Cenozoic era is known as?
water resources acquisition fees (WRAF)
fees paid by new developments for their proportionate share of the costs associated with making water supplies available
water reuse
also known as water reclamation or water recycling
water rights transfer
legally recognized and enforceable permanent or leased change of a water right to enhance ecosystem function
Another name for deuterium oxide is?
water self-sufficiency
using water produced only from local groundwater and other local sources and maintaining a resilient system to meet water demands
watershed
drainage basin area contributing water to a network of stream channels, a lake or other areas where water can collect
water storage gap
the difference between the amount of water storage needed and the amount of natural and human-made water storage
water stress
occurs when water demand exceeds available amount during a certain period or when poor quality restricts its use
water table
the level below which the ground is saturated with water
water duty
amount of water that is reasonable to apply to irrigated land to produce crops based on location, soil, consumptive use, evaporation and seepage
water equity
occurs when all communities have access to safe, clean, affordable drinking water and wastewater services,
participate in community water-related decision-making processes related to water and share in the economic, social and environmental benefits of water systems
water harvesting
process of intercepting stormwater from a surface, such as a roof, parking area, or land surface, and putting it to beneficial use
water-intensive landscaped area
any area of land that is not planted with ADWR's Low Water Use/Drought Tolerant Plant list
waterpocket
refers to the potholes that dot sandstone and fill with rainwater
water quality
the chemical, physical and biological characteristics of water based on usage standards
water reclamation
also known as water recycling or water reuse, reclaims water from a variety of sources then treats and reuses it for agriculture and irrigation,
potable water supplies, groundwater replenishment, industrial processes and environmental restoration
water recycling
also known as water reclamation or water reuse
The Cenozoic era is known as?
water resources acquisition fees (WRAF)
fees paid by new developments for their proportionate share of the costs associated with making water supplies available
water reuse
also known as water reclamation or water recycling
water rights transfer
legally recognized and enforceable permanent or leased change of a water right to enhance ecosystem function
Another name for deuterium oxide is?
water self-sufficiency
using water produced only from local groundwater and other local sources and maintaining a resilient system to meet water demands
watershed
drainage basin area contributing water to a network of stream channels, a lake or other areas where water can collect
water storage gap
the difference between the amount of water storage needed and the amount of natural and human-made water storage
water stress
occurs when water demand exceeds available amount during a certain period or when poor quality restricts its use
water table
the level below which the ground is saturated with water


 wind rose
a chart showing the relative frequency of wind directions at a place
withdrawal
water removed from the ground
X ↑
xeriscaping
landscaping requiring little or no irrigation
Y ↑
w
yield
mass per unit time per unit area
Z ↑
zinc
a bluish-white, ductile metallic element when pure and heated, brittle at ordinary temperatures, an essential micronutrient for both plants and animals, used especially in alloys and as a protective coating in galvanizing iron and steel
wind rose
a chart showing the relative frequency of wind directions at a place
withdrawal
water removed from the ground
X ↑
xeriscaping
landscaping requiring little or no irrigation
Y ↑
w
yield
mass per unit time per unit area
Z ↑
zinc
a bluish-white, ductile metallic element when pure and heated, brittle at ordinary temperatures, an essential micronutrient for both plants and animals, used especially in alloys and as a protective coating in galvanizing iron and steel